13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(26):11863-11880. doi:10.7150/thno.49069 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ceria-based nanotheranostic agent for rheumatoid arthritis
1. Department of Biomedical Engineering and the Institute for Quantitative Health Science & Engineering.
2. Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
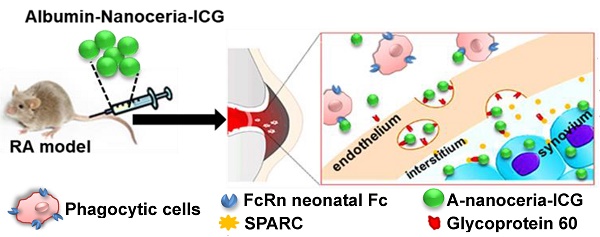
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that affects 1-2% of the human population worldwide, and effective therapies with targeted delivery for local immune suppression have not been described. We address this problem by developing a novel theranostic nanoparticle for RA and assessed its therapeutic and targeting effects under image-guidance.
Methods: Albumin-cerium oxide nanoparticles were synthesized by the biomineralization process and further conjugated with near-infrared, indocyanine green (ICG) dye. Enzymatic-like properties and reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging activities, as well as the ability to reprogram macrophages, were determined on a monocyte cell line in culture. The therapeutic effect and systemic targeting potential were evaluated in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model using optical/optoacoustic tomographic imaging.
Results: Small nanotheranostics with narrow size distribution and high colloidal stability were fabricated and displayed high ROS scavenging and enzymatic-like activity, as well as advanced efficacy in a converting pro-inflammatory macrophage phenotype into anti-inflammatory phenotype. When administrated into affected animals, these nanoparticles accumulated in inflamed joints and revealed a therapeutic effect similar to the gold-standard therapy for RA, methotrexate.
Conclusions: The inflammation-targeting, inherent contrast and therapeutic activity of this new albumin-cerium oxide nanoparticle may make it a relevant agent for assessing severity in RA, and other inflammatory diseases, and controlling inflammation with image-guidance. The design of these nanotheranostics will enable potential clinical translation as systemic therapy for RA.
Keywords: theranostics, nanoceria, albumin nanoparticles, rheumatoid arthritis, ICG, imaging
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact