13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(25):11754-11774. doi:10.7150/thno.43163 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Cardiomyocyte-derived small extracellular vesicles can signal eNOS activation in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells to protect against Ischemia/Reperfusion injury
1. State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Disease, Department of Cardiology, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100037, China
2. Department of Internal Medicine (Cardiology), University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX 75390-8573, USA
3. Department of Medical Ultrasound, Institute of Diagnostic and Interventional Ultrasound, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510080, China
4. Department of Cardiology, Biomedical Research (Therapy) Center, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310020, China
5. Center for Cardiac Intensive Care, Beijing Anzhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing Institute of Heart, Lung and Blood Vessel Diseases, Beijing 100029, China
6. Yiling Hospital of Hebei Medical University, National Key Laboratory of Collateral Disease Research and Innovative Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050035, China
7. National Key Laboratory of Collateral Disease Research and Innovative Chinese Medicine, Key Laboratory of State Administration of TCM (Cardio-Cerebral Vessel Collateral Disease), Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050035, China
Abstract
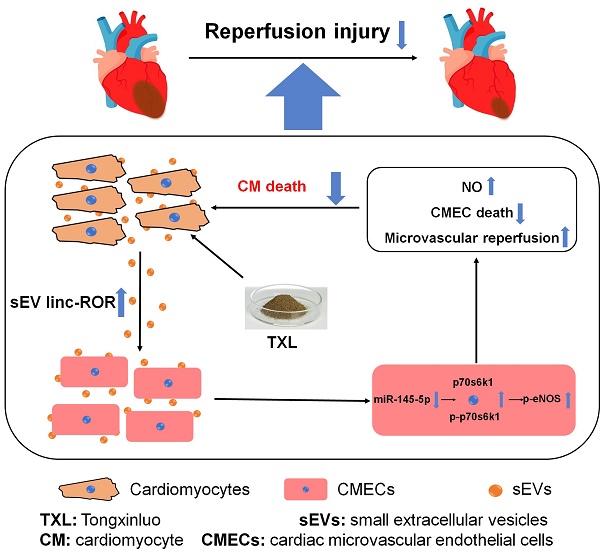
Rationale: The crosstalk between cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (CMECs) and cardiomyocytes (CMs) has emerged as a key component in the development of, and protection against, cardiac diseases. For example, activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in CMECs, by therapeutic strategies such as ischemic preconditioning, plays a critical role in the protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. However, much less is known about the signals produced by CMs that are able to regulate CMEC biology. Here we uncovered one such mechanism using Tongxinluo (TXL), a traditional Chinese medicine, that alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury by activating CMEC eNOS. The aim of our study is to identify the signals produced by CMs that can regulate CMEC biology during I/R.
Methods: Ex vivo, in vivo, and in vitro settings of ischemia-reperfusion were used in our study, with the protective signaling pathways activated in CMECs identified using genetic inhibition (p70s6k1 siRNA, miR-145-5p mimics, etc.), chemical inhibitors (the eNOS inhibitor, L-NNA, and the small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) inhibitor, GW4869) and Western blot analyses. TritonX-100 at a dose of 0.125% was utilized to inactivate the eNOS activity in endothelium to investigate the role of CMEC-derived eNOS in TXL-induced cardioprotection.
Results: We found that while CMEC-derived eNOS activity was required for the cardioprotection of TXL, activation of eNOS in CMECs by TXL did not occur directly. Instead, eNOS activation in CMECs required a crosstalk between CMs and CMECs through the uptake of CM-derived sEVs. We further demonstrate that TXL induced CM-sEVs contain increased levels of Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA, Regulator Of Reprogramming (Linc-ROR). Upon uptake into CMECs, linc-ROR downregulates its target miR-145-5p leading to activation of the eNOS pathway by facilitating the expression of p70s6k1 in these cells. The activation of CMEC-derived eNOS works to increase survival in both the CMECs and the CMs themselves.
Conclusions: These data uncover a mechanism by which the crosstalk between CMs and CMECs leads to the increased survival of the heart after I/R injury and point to a new therapeutic target for the blunting of myocardial I/R injury.
Keywords: Cardioprotection, tongxinluo, cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, crosstalk
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact