13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(25):11549-11561. doi:10.7150/thno.44251 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CXCR4 induces cell autophagy and maintains EBV latent infection in EBVaGC
1. Department of Pathogeny Biology, Basic Medicine College,Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, China.
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Zibo Central Hospital, ZiBo 255000, China.
3. Department of Pathology, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, China.
Abstract
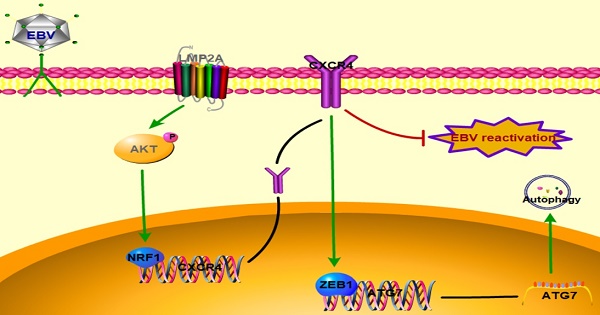
Rationale: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is found in ~7% of gastric carcinoma cases worldwide, and all tumour cells harbour the clonal EBV genome. EBV can regulate pathways and protein expression to induce gastric carcinoma; however, the molecular mechanism underlying EBV-associated gastric carcinoma (EBVaGC) remains elusive.
Methods: GEO microarray and molecular experiments were performed to compare CXCR4 expression between EBV-positive and EBV-negative gastric carcinoma (EBVnGC). Transfections with LMP2A plasmid or siRNA were carried out to assess the role of LMP2A in CXCR4 expression. The effects and mechanisms of CXCR4 on cell autophagy were analysed in vitro using molecular biological and cellular approaches. Additionally, we also determined the regulatory role of CXCR4 in latent EBV infection.
Results: CXCR4 expression was significantly upregulated in EBVaGC tissues and cell lines. LMP2A could induce AKT phosphorylation to increase NRF1 expression, thereby binding to the CXCR4 promoter to increase its transcriptional level. Moreover, CXCR4 promoted ZEB1 expression to upregulate ATG7 synthesis, which could then activate autophagy. Moreover, CXCR4 increased the number of cells entering the G2/M phase and inhibited cell apoptosis via the autophagy pathway. Finally, CXCR4 knockdown was associated with elevated BZLF1 expression, but this effect was not influenced by autophagy.
Conclusions: Our data suggested new roles for CXCR4 in autophagy and EBV replication in EBVaGC, which further promoted cell survival and persistent latent infection. These new findings can lead to further CXCR4-based anticancer therapy.
Keywords: CXCR4, EBV, EBVaGC, Autophagy, BZLF1
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact