13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(24):11197-11214. doi:10.7150/thno.44920 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ZnO-based multifunctional nanocomposites to inhibit progression and metastasis of melanoma by eliciting antitumor immunity via immunogenic cell death
1. Department of Dermatology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST), Wuhan 430022, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Material Chemistry for Energy Conversion and Storage, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, HUST, Wuhan 430074, China.
3. Department of Hematology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, HUST, Wuhan 430022, China.
4. Department of Dermatology, The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Tongji Medical College, HUST, Wuhan 430022, China.
5. Clinical Laboratory, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, HUST, Wuhan 430022, China.
6. Department of Dermatology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST), Wuhan 430022, China.
7. Department of Dermatology, Rutgers-RWJMS, Somerset, New Jersey, USA.
8. Department of Dermatology, XiangYa Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China.
9. Department of Immunology, Tongji Medical College, HUST, Wuhan 430022, China.
Abstract
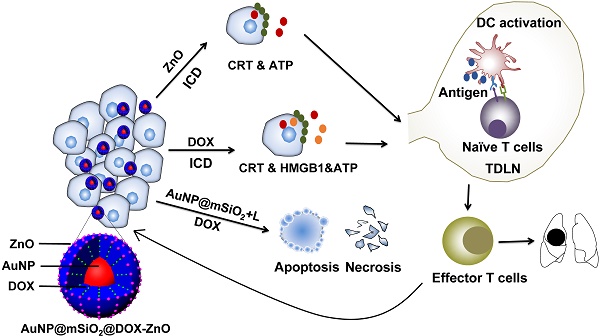
Rationale: The development of a highly effective and tumor-specific therapeutic strategy, which can act against the primary tumor and also condition the host immune system to eliminate distant tumors, remains a clinical challenge.
Methods: Herein, we demonstrate a facile yet versatile ZnO-capping and Doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded multifunctional nanocomposite (AuNP@mSiO2@DOX-ZnO) that integrates photothermal properties of gold nanoparticles (NPs), pH-responsive properties and preferential selectivity to tumor cells of ZnO QDs and chemotherapeutic agent into a single NP. The photothermal performance, pH-triggered release and preferential phagocytic ability were assessed. The induced anti-tumor immunity was determined by analyzing immune cell profile in tumor in vivo and molecular mechanism were identified by detecting expression of immunogenic cell death (ICD) markers in vitro. Moreover, mice models of unilateral and bilateral subcutaneous melanoma and lung metastasis were established to evaluate the antitumor effects.
Results: As an efficient drug carrier, ZnO-capped NPs guarantee a high DOX payload and an in vitro, efficient release of at pH 5.0. In murine melanoma models, the nanocomposite can significantly inhibit tumor growth for a short period upon low-power laser irradiation. Importantly, ZnO NPs not only demonstrate preferential selectivity for melanoma cells but can also induce ICD. Meanwhile, AuNP@mSiO2-based photothermal therapy (PTT) and DOX are directly cytotoxic towards cancer cells and demonstrate an elevated ICD effect. The induced ICD promotes maturation of dendritic cells, further stimulating the infiltration of effector T cells into tumor sites, preventing tumor growth and distant lung metastases.
Conclusions: This study highlights the novel mechanism of ZnO-triggered anti-tumor immunity via inducing ICD. Additionally, we shed light on the multifunctionality of nanocomposites in delivering localized skin tumor therapy as well as inhibiting metastatic growth, which holds great promise in clinical applications.
Keywords: ZnO Nanoparticles, Immunogenic Cell Death, Thermo-chemotherapy, Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles, Melanoma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact