13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(23):10619-10633. doi:10.7150/thno.44871 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CDK4/6 inhibition promotes immune infiltration in ovarian cancer and synergizes with PD-1 blockade in a B cell-dependent manner
1. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Xijing Hospital, The Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an, China;
2. Department of Spine Surgery, Honghui Hospital, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China;
3. School of Public Health, College of Medicine, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China;
4. State Key Laboratory of Cancer Biology, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, The Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
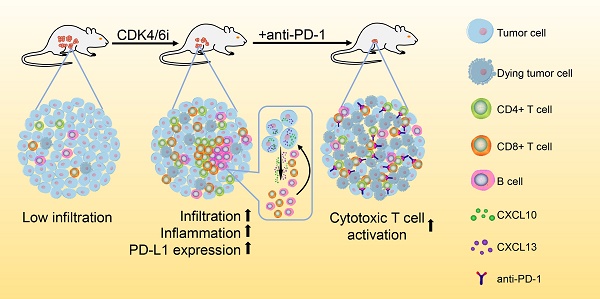
Great progress has been made in the field of tumor immunotherapy in the past decade. However, the therapeutic effects of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) against ovarian cancer are still limited. Recently, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6i) has been reported to enhance antitumor immunity in preclinical models. The combined use of CDK4/6i and ICB may be beneficial, but the effects of CDK4/6is on the tumor immune microenvironment and whether they can synergize with ICB in treating ovarian cancer remain unknown.
Methods: In this study, we first assessed the antitumor efficacy of abemaciclib, an FDA-approved CDK4/6i, in a syngeneic murine ovarian cancer model. Then, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence and flow cytometry were performed to evaluate the number, proportion, and activity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Cytokine and chemokine production was detected both in vivo and in vitro by PCR array analysis and cytokine antibody arrays. The treatment efficacy of combined abemaciclib and anti-PD-1 therapy was evaluated in vivo, and CD8+ and CD4+ T cell activities were analyzed using flow cytometry. Lastly, the requirement for both CD8+ T cells and B cells in combination treatment was evaluated in vivo, and potential cellular mechanisms were further analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: We observed that abemaciclib monotherapy could enhance immune infiltration, especially CD8+ T cell and B cell infiltration, in the ID8 murine ovarian cancer model. Immunophenotyping analysis showed that abemaciclib induced a proinflammatory immune response in the tumor microenvironment. PCR array analysis suggested the presence of a Th1-polarized cytokine profile in abemaciclib-treated ID8 tumors. In vitro studies showed that abemaciclib-treated ID8 cells secreted more CXCL10 and CXCL13, thus recruiting more lymphocytes than control groups. Combination treatment achieved better tumor control than monotherapy, and the activities of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells were further enhanced when compared with monotherapy. The synergistic antitumor effects of combined abemaciclib and anti-PD-1 therapy depended on both CD8+ T cells and B cells.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that combined treatment with CDK4/6i and anti-PD-1 antibody could improve the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy and hold great promise for the treatment of poorly immune-infiltrated ovarian cancer.
Keywords: CDK4/6, immune infiltration, chemokine, PD-1, ovarian cancer
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact