13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(1):247-264. doi:10.7150/thno.37200 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ASIC1a induces synovial inflammation via the Ca2+/NFATc3/ RANTES pathway
1. Anhui Key Laboratory of Bioactivity of Natural Products, School of Pharmacy, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, China;
2. The Key Laboratory of Anti-inflammatory and Immune Medicine, Anhui Medical University, Ministry of Education, Hefei 230032, China.
Abstract
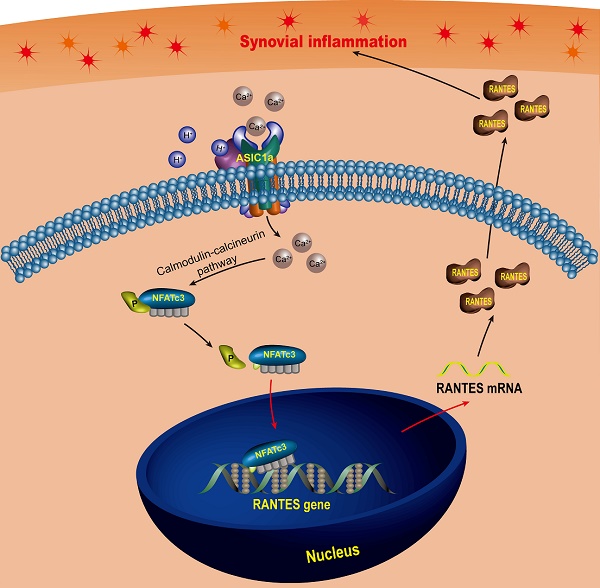
Rationale: Synovial inflammation is one of the main pathological features of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and is a key factor leading to the progression of RA. Understanding the regulatory mechanism of synovial inflammation is crucial for the treatment of RA. Acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a) is an H+-gated cation channel that promotes the progression of RA, but the role of ASIC1a in synovial inflammation is unclear. This study aimed to investigate whether ASIC1a is involved in the synovial inflammation and explore the underlying mechanisms in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: The expression of ASIC1a and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFATs) were analyzed by Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry both in vitro and in vivo. The Ca2+ influx mediated by ASIC1a was detected by calcium imaging and flow cytometry. The role of ASIC1a in inflammation was studied in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis (AA). Inflammatory cytokine profile was analyzed by protein chip in RA synovial fibroblasts (RASF) and verified by a magnetic multi-cytokine assay and ELISA. The NFATc3-regulated RANTES (Regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted) gene transcription was investigated by ChIP-qPCR and dual-luciferase reporter assay.
Results: The expression of ASIC1a was significantly increased in human RA synovial tissues and primary human RASF as well as in ankle synovium of AA rats. Activated ASIC1a mediated Ca2+ influx to increase [Ca2+]i in RASF. The activation/overexpression of ASIC1a in RASF up-regulated the expression of inflammatory cytokines RANTES, sTNF RI, MIP-1a, IL-8, sTNF RII, and ICAM-1 among which RANTES was increased most remarkably. In vivo, ASIC1a promoted inflammation, synovial hyperplasia, articular cartilage, and bone destruction, leading to the progression of AA. Furthermore, activation of ASIC1a upregulated the nuclear translocation of NFATc3, which bound to RANTES promoter and directly regulated gene transcription to enhance RANTES expression.
Conclusion: ASIC1a induces synovial inflammation, which leads to the progression of RA. Our study reveals a novel RA inflammation regulatory mechanism and indicates that ASIC1a might be a potential therapeutic target for RA.
Keywords: ASIC1a, inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, NFATc3
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact