13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(24):7447-7457. doi:10.7150/thno.34883 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine mediates active targeting of human serum albumin in U87MG xenograft mouse models
1. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University Graduate School, Seoul, Republic of Korea
3. Tumor Biology Program, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
4. Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
5. Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
6. Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Graduated School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
7. Tumor Microenvironment Global Core Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
8. Institute of Radiation Medicine, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
9. Cancer Imaging Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
10. Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
11. Ischemic/Hypoxic Disease Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
12. Department of Nuclear Medicine, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Republic of Korea
* These authors contributed equally to this research.
Abstract
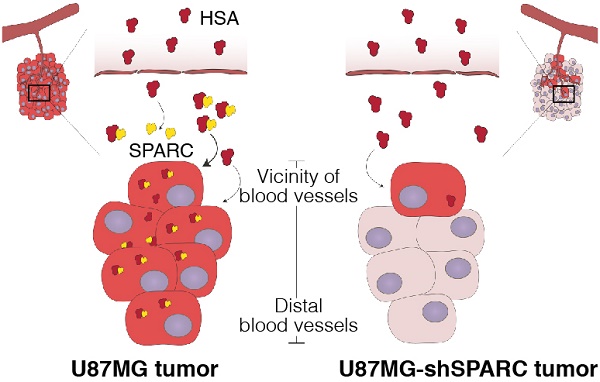
Human serum albumin (HSA) is the most abundant plasma protein. The main reason for using HSA as a versatile tool for drug delivery is based on its ability to accumulate in tumors. However, the mechanism of albumin accumulation in tumors is not yet clear. Many researchers using HSA as a drug-carrier have focused on the passive tumor targeting by enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, while other investigators proposed that albumin binding proteins mediate albumin accumulation in tumors. We investigated whether HSA accumulation in tumors is mediated by the EPR effect or by secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC), which is known to be an albumin-binding protein.
Methods: To investigate the role of SPARC on HSA accumulation in tumors, we compared HSA uptake in U87MG glioblastoma cells with different SPARC expression. U87MG cells generally express high levels of SPARC and were, therefore, used as SPARC-rich cells. SPARC-less U87MG (U87MG-shSPARC) cells were established by viral-shSPARC transduction. We detected cellular uptake of fluorescence-labeled HSA by confocal microscopy in U87MG and U87MG-shSPARC cells. To demonstrate the mechanism of HSA accumulation in tumors, we injected FNR648-labeled HSA and FITC-labeled dextran in U87MG and U87MG-shSPARC tumor-bearing mice and observed their micro-distribution in tumor tissues.
Results: HSA was internalized in cells by binding with SPARC in vitro. HSA accumulation in U87MG glioma was associated with SPARC expression in vivo. FITC-dextran was distributed in U87MG tumors in the vicinity of blood vessels. The distribution of HSA, on the other hand, was observed in the regions remote from blood vessels of U87MG tumor tissues but not in U87MG-shSPARC tumor tissues.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that the tumor-distribution of HSA is affected not only by the EPR-effect but also by SPARC expression. SPARC enhances HSA accumulation in U87MG glioma and mediates active targeting of HSA in tumors.
Keywords: human serum albumin, SPARC, cancer imaging, tumor targeting, glioma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact