13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(23):6962-6975. doi:10.7150/thno.35084 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Rational design of caspase-responsive smart molecular probe for positron emission tomography imaging of drug-induced apoptosis
1. Key Laboratory of Nuclear Medicine of Ministry of Health, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Nuclear Medicine, Jiangsu Institute of Nuclear Medicine, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
2. Department of Medical Imaging, Jinling Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
3. Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University Medical Center Rotterdam, Erasmus MC, Wytemaweg 80, 3015 CN Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Abstract
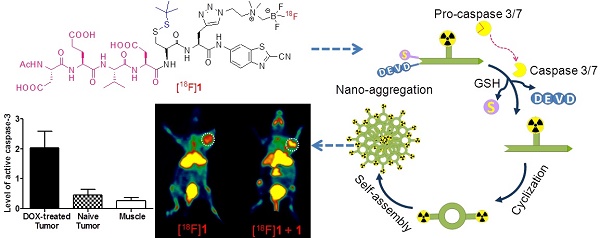
Purpose: Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of apoptosis is very important for early evaluation of tumor therapeutic efficacy. A stimuli-responsive probe based on the peptide sequence Asp-Glu-Val-Asp (DEVD), [18F]DEVD-Cys(StBu)-PPG(CBT)-AmBF3 ([18F]1), for PET imaging of tumor apoptosis was designed and prepared. This study aimed to develop a novel smart probe using a convenient radiosynthesis method and to fully examine the sensitivity and specificity of the probe response to the tumor treatment.
Methods: The radiolabelling precursor DEVD-Cys(StBu)-PPG(CBT)-AmBF3 (1) was synthesized through multistep reactions. The reduction together with caspase-controlled macrocyclization and self-assembly of 1 was characterized and validated in vitro. After [18F]fluorination in the buffer (pH= 2.5), the radiolabelling yield (RLY), radiochemical purity (RCP) and stability of the probe [18F]1 in PBS and mouse serum were investigated by radio-HPLC. The sensitivity and specificity of [18F]1 for detecting the drug-induced apoptosis was fully evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The effect of cold precursor 1 on the cell uptake and tumor imaging of [18F]1 was also assessed. The level of activated caspase-3 in Hela cells and tumors with or without apoptosis induction was analyzed and compared by western blotting and histological staining.
Results: The whole radiosynthesis process of [18F]1 was around 25 min with RLY of 50%, RCP of over 99% and specific activity of 1.45 ± 0.4 Ci/µmol. The probe was very stable in both PBS and mouse serum within 4 h. It can be activated by caspase-3 and then undergo an intermolecular cyclization to form nanosized particles. The retained [18F]1 in DOX-treated HeLa cells was 2.2 folds of that in untreated cells. Within 1 h microPET imaging of the untreated Hela-bearing mice, the injection of [18F]1 resulted in the increase of the uptake ratio of tumor to muscle (T/M) only from 1.74 to 2.18, while in the DOX-treated Hela-bearing mice T/M increased from 1.88 to 10.52 and the co-injection of [18F]1 and 1 even led to the increase of T/M from 3.08 to 14.81.
Conclusions: A caspase-responsive smart PET probe [18F]1 was designed and prepared in a kit-like manner. Co-injection of [18F]1 and 1 generated remarkably enhanced tumor uptake and signal-to-noise ratio in the tumor-bearing mice with drug-induced apoptosis, which correlated well with the expression level of activated caspase-3. This early readout of treatment response ensured that the probe [18F]1 could serve as a promising PET imaging probe for timely and noninvasive evaluation of tumor therapy.
Keywords: positron emission tomography (PET), smart molecular probe, caspase-responsive, apoptosis, rapid [18F]fluorination
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact