13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(20):5755-5768. doi:10.7150/thno.36163 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Stimuli-responsive nanodrug self-assembled from amphiphilic drug-inhibitor conjugate for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer treatment
1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Metal Matrix Composites, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai 200240, P. R. China
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Fengxian Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shanghai 201499, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
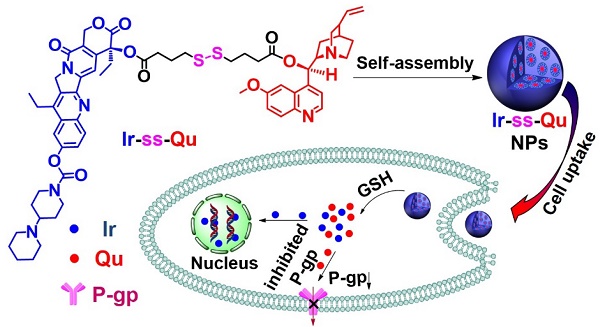
Severe multidrug resistance (MDR) often develops in the process of chemotherapy for most small molecule anticancer drugs, which results in clinical chemotherapy failures.
Methods: Here, a nanodrug is constructed through the self-assembly of amphiphilic drug-inhibitor conjugates (ADIC) containing a redox-responsive linkage for reversing the multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer treatment. Specifically, hydrophilic anticancer irinotecan (Ir) and hydrophobic P-gp protein inhibitor quinine (Qu) are linked by a redox responsive bridge for overcoming MDR of tumors.
Results: Ir-ss-Qu is able to self-assemble into nanoparticles (NPs) in water and shows the longer blood retention half-life compared with that of free Ir or Qu, which facilitates drug accumulation in tumor site. After endocytosis of Ir-ss-Qu NPs by drug-resistant tumor cells, the disulfide bond in the linkage between Ir and Qu is cleaved rapidly induced by glutathione (GSH) to release anticancer drug Ir and inhibitor Qu synchronously. The released Qu can markedly reduce the expression of P-gp in drug-resistant tumor cells and inhibits P-gp to pump Ir out of the cells. The increased concentration of intracellular Ir can effectively improve the therapeutic efficacy.
Conclusions: Such redox-responsive Ir-ss-Qu NPs, as a drug delivery system, exhibit very high cytotoxicity and the most effective inhibitory to the growth of drug-resistant breast cancer compared with that of free therapeutic agents in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: multidrug resistance, stimuli-responsive, drug-inhibitor conjugate, self-assembly, nanodrug
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact