13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(19):5424-5442. doi:10.7150/thno.33015 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Intelligent gold nanostars for in vivo CT imaging and catalase-enhanced synergistic photodynamic & photothermal tumor therapy
1. Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics at Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics-Hubei Bioinformatics & Molecular Imaging Key Laboratory, Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, Hubei, P. R. China
2. Key Laboratory of Biomedical Photonics (HUST), Ministry of Education, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, Hubei, P. R. China
3. Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Nutrition University of Maryland, School of Medicine Baltimore, MD 21201, USA
Abstract
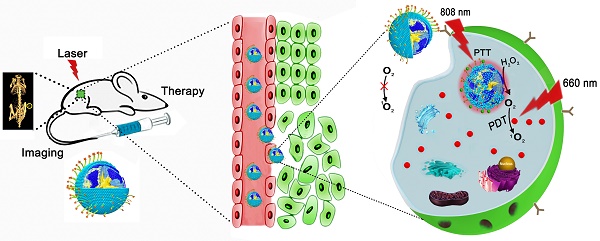
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a clinically approved and minimally invasive form of cancer treatment. However, due to hypoxia at the tumor site and phototoxicity to normal tissues, monotherapies using photosensitizers remain suboptimal. This study aimed to develop a highly selective controlled catalase-enhanced synergistic photodynamic and photothermal cancer therapy based on gold nanostars.
Methods: Gold nanostars (GNS) with high thermal conversion efficiency were used as the core for photothermal therapy (PTT) and the shell consisted of the photosensitizer Ce6-loaded mesoporous silicon. The shell was modified with catalase (E), which catalyzes the conversion of hydrogen peroxide to oxygen at the tumor site, alleviating hypoxia and increasing the effect of the photodynamic treatment. Finally, a phospholipid derivative with c(RGDyK) was used as the targeting moiety and the nanoparticle-encapsulating material.
Results: The nanoprobe exhibited good dispersion, high stability, and high photothermal conversion efficiency (~28%) for PTT as well as a photodynamic "on-off" effect on Ce6 encapsulated in mesoporous channels. The "release" of Ce6 was only triggered under photothermal stimulation in vivo. Due to its targeting ability, 72 h after injection of the probe, the tumor site in mice showed an observable CT response. The combined treatment using photothermal therapy (PTT) and catalase-enhanced photo-controlled PDT exerted a superior effect to PTT or PDT monotherapies.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that the use of this intelligent nanoprobe for CT-targeted image-guided treatment of tumors with integrated photothermal therapy (PTT) and catalase-enhanced controlled photodynamic therapy (PDT) may provide a novel approach for cancer theranostics.
Keywords: CT imaging, catalase, hypoxia, photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, singlet oxygen
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact