13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(16):4704-4716. doi:10.7150/thno.34588 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MicroRNA Biogenesis is Enhanced by Liposome-Encapsulated Pin1 Inhibitor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, National Clinical Research Center for Geriatrics, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, Sichuan, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Bio-Resource and Eco-Environment of Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China.
3. West China School of Basic Medical Sciences & Forensic Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
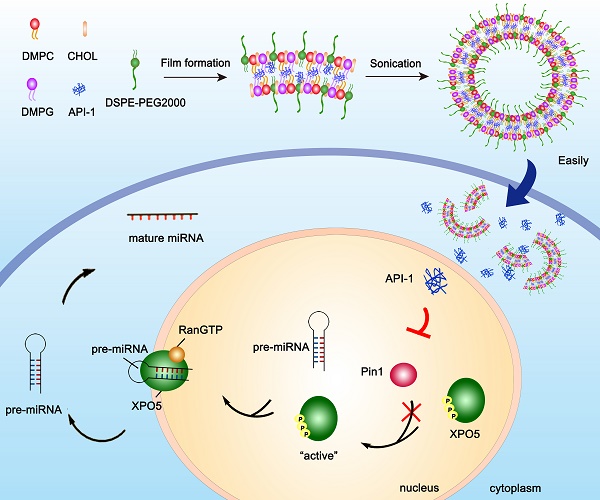
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is in an urgent need of new, effective therapies to reduce morbidity and mortality. We have previously demonstrated that peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase Pin1 is a potential target for HCC therapy, due to its pivotal role in HCC development through regulating miRNA biogenesis, and discovered the small molecule API-1 as a novel and specific Pin1 inhibitor. Despite its significant anti-HCC activity, the low water solubility and in vivo bioavailability of API-1 limit its clinical application. To address these issues, we herein developed a liposomal formulation of API-1 to improve API-1 delivery and enhance its anti-HCC efficacy.
Methods: We designed and developed a nanoscale liposomal formulation of API-1, named as API-LP. Subsequently, the mean diameter, polydispersity, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency and thermal properties of the optimization API-LP were characterized. The enhanced anti-HCC activity and the molecular mechanism of API-LP were investigated both in vitro and in vivo. Finally, the safety and pharmacokinetic property of API-LP were evaluated systematically.
Results: API-LP had good formulation characteristics and exhibited an enhanced in vitro activity of suppressing proliferation and migration of HCC cells when compared with free API-1. The mechanism study showed that API-LP upregulated miRNA biogenesis via inhibiting Pin1 activity followed by restoring the nucleus-to-cytoplasm export of XPO5. Because of the increased delivery efficiency, API-LP displayed a stronger ability to promote miRNA biogenesis than free API-1. Importantly, API-LP displayed higher systemic exposure than free API-1 in mice without apparent toxicity, resulting in an enhanced tumor inhibition in xenograft mice.
Conclusion: The development and assessment of API-LP provide an attractive and safe anti-HCC agent, highlighting the miRNA-based treatment for human cancers.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, Pin1, API-1, liposome, targeted therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact