13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(13):3853-3865. doi:10.7150/thno.31868 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The m6A demethylase ALKBH5 controls trophoblast invasion at the maternal-fetal interface by regulating the stability of CYR61 mRNA
1. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 201204, P.R. China.
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the Shanghai Jiaotong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai 200233, P.R. China.
3. The International Peace Maternity & Child Health Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200030, P. R. China.
4. Clinical and Translational Research Center, Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200040, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
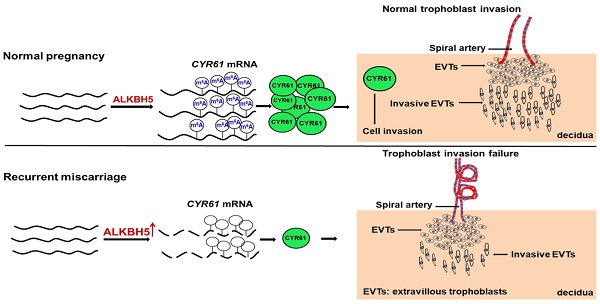
N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent internal modification in mammalian mRNAs. Although m6A is important in many biological processes, its roles in the placenta are unclear.
Methods: Levels of global mRNA m6A methylation and ALKBH5 expression in recurrent miscarriage (RM) patients were determined using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR), m6A RNA methylation quantification, and immunohistochemical methods. Using ALKBH5 overexpression and knockdown methods, we determined the role of ALKBH5 in trophoblast invasion at the maternal interface through trophoblasts and an extravillous explant culture experiments. Furthermore, the regulation of CYR61 by ALKBH5 was explored by RNA-sequencing coupled with methylated RNA immunoprecipitation.
Results: We found that the level of global mRNA m6A methylation was significantly decreased in placental villous tissue from RM patients, while ALKBH5 expression was specifically unregulated. Furthermore, we demonstrated that ALKBH5 knockdown in human trophoblast promoted trophoblast invasion. Conversely, overexpression of ALKBH5 inhibited cell invasion. ALKBH5 knockdown promoted trophoblast invasion in villous explant culture experiments, while overexpression of ALKBH5 repressed these effects. Furthermore, we clarified that ALKBH5 inhibited trophoblast invasion by regulating CYR61 mRNA stability, and this RNA regulation is m6A dependent. Mechanistic analyses showed that decreased ALKBH5 in trophoblast increased the half-life of CYR61 mRNA and promoted steady-state CYR61 mRNA expression levels.
Conclusions: We elucidated the functional roles of ALKBH5 and mRNA m6A methylation in trophoblast and identified a novel RNA regulatory mechanism, providing a basis for further exploration of broad RNA epigenetic regulatory patterns in RM diseases.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine, ALKBH5, CYR61, trophoblast invasion, recurrent miscarriage.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact