13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(13):3768-3779. doi:10.7150/thno.34327 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Melatonin enhances sorafenib-induced cytotoxicity in FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia cells by redox modification
1. Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center; State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China; Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou 510060, China
2. Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510000, China.
3. The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China
4. Department of Leukemia, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas 77030, USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
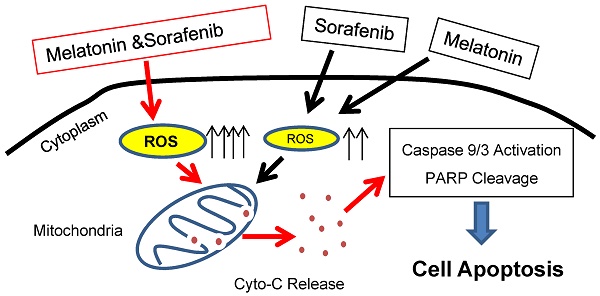
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with an internal tandem duplication in Fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3-ITD) is identified as a subgroup with poor outcome and intrinsic resistance to chemotherapy and therefore urgent need for development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Methods: The antitumor effects of melatonin alone or combined with sorafenib were evaluated via flow cytometry and immunoblotting assays in FLT-ITD AML cells. Also, the ex vivo and in vivo models were used to test the synergistic effects of melatonin and sorafenib against leukemia with FLT3/ITD mutation.
Results: Our study shows for the first time that melatonin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in FLT3/ITD-positive leukemia cells. Mechanistically, melatonin preferentially causes overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ultimately massive cell death in FLT3-ITD AML cells. Moreover, melatonin significantly enhances the cytotoxicity induced by the FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib in AML cells with FLT3/ITD through redox modification. Importantly, combination of melatonin and sorafenib exhibited highly synergistic therapeutic activity in MV4-11 xenografts and a murine model bearing FLT3/ITD leukemia.
Conclusion: This study indicates that melatonin, alone or in combination with sorafenib, has potential to improve the therapeutic outcome of AML patients with FLT3-ITD mutation that merits further investigation.
Keywords: Melatonin, Sorafenib, FLT3-ITD, Leukemia, Redox modification
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact