13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(11):3017-3040. doi:10.7150/thno.31913 This issue Cite
Review
Integrating Stimuli-Responsive Properties in Host-Guest Supramolecular Drug Delivery Systems
Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN 46556 USA
Abstract
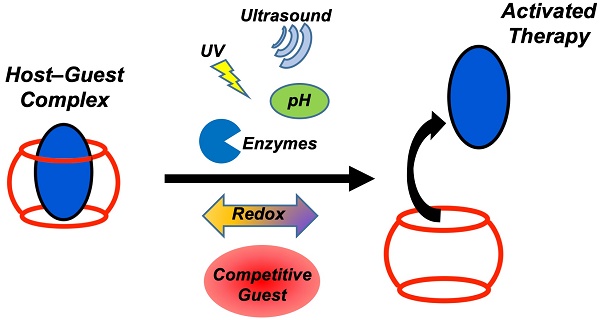
Host-guest motifs are likely the most recognizable manifestation of supramolecular chemistry. These complexes are characterized by the organization of small molecules on the basis of preferential association of a guest within the portal of a host. In the context of their therapeutic use, the primary application of these complexes has been as excipients which enhance the solubility or improve the stability of drug formulations, primarily in a vial. However, there may be opportunities to go significantly beyond such a role and leverage key features of the affinity, specificity, and dynamics of the interaction itself toward “smarter” therapeutic designs. One approach in this regard would seek stimuli-responsive host-guest recognition, wherein a complex forms in a manner that is sensitive to, or can be governed by, externally applied triggers, disease-specific proteins and analytes, or the presence of a competing guest. This review will highlight the general and phenomenological design considerations governing host-guest recognition and the specific types of chemistry which have been used and are available for different applications. Finally, a discussion of the molecular engineering and design approaches which enable sensitivity to a variety of different stimuli are highlighted. Ultimately, these molecular-scale approaches offer an assortment of new chemistry and material design tools toward improving precision in drug delivery.
Keywords: Crown ether, porphyrin, calixarenes, pillararenes, cyclodextrin, cucurbituril, rotaxane
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact