13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(8):2282-2298. doi:10.7150/thno.30621 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of protein disulfide isomerase in glioblastoma causes marked downregulation of DNA repair and DNA damage response genes
1. Department of Medicinal Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, Rogel Cancer Center, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
2. Radiation Oncology, Rogel Cancer Center, Center for RNA, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
3. National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, CAS Center for Excellence in Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
4. Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
5. Department of Computational Medicine and Bioinformatics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
6. Environmental Health Sciences, Rogel Cancer Center, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
7. College of Life Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 10049, China
Abstract
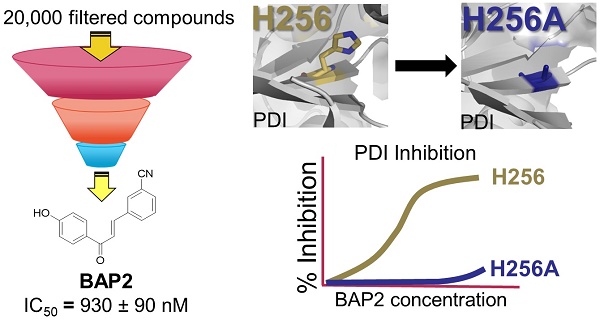
Aberrant overexpression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident oxidoreductase protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) plays an important role in cancer progression. In this study, we demonstrate that PDI promotes glioblastoma (GBM) cell growth and describe a class of allosteric PDI inhibitors that are selective for PDI over other PDI family members.
Methods: We performed a phenotypic screening triage campaign of over 20,000 diverse compounds to identify PDI inhibitors cytotoxic to cancer cells. From this screen, BAP2 emerged as a lead compound, and we assessed BAP2-PDI interactions with gel filtration, thiol-competition assays, and site-directed mutagenesis studies. To assess selectivity, we compared BAP2 activity across several PDI family members in the PDI reductase assay. Finally, we performed in vivo studies with a mouse xenograft model of GBM combining BAP2 and the standard of care (temozolomide and radiation), and identified affected gene pathways with nascent RNA sequencing (Bru-seq).
Results: BAP2 and related analogs are novel PDI inhibitors that selectively inhibit PDIA1 and PDIp. Though BAP2 contains a weak Michael acceptor, interaction with PDI relies on Histidine 256 in the b' domain of PDI, suggesting allosteric binding. Furthermore, both in vitro and in vivo, BAP2 reduces cell and tumor growth. BAP2 alters the transcription of genes involved in the unfolded protein response, ER stress, apoptosis and DNA repair response.
Conclusion: These results indicate that BAP2 has anti-tumor activity and the suppressive effect on DNA repair gene expression warrants combination with DNA damaging agents to treat GBM.
Keywords: Protein disulfide isomerase, drug discovery, allosteric inhibition, cancer, DNA repair
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact