13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(6):1683-1697. doi:10.7150/thno.30487 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Characterization and Therapeutic Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Neuromesodermal Origin from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
1. Center for Stem Cell Biology and Tissue Engineering, Key Laboratory for Stem Cells and Tissue Engineering, Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, P.R. China.
2. Department of Pediatric Surgery, Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, P.R. China
3. Department of Cell Biology, Zhongshan Medical School, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, P.R.China.
4. Department of Orthopedics, The Eighth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518033, P.R.China.
5. Department of Biochemistry, Zhongshan Medical School, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, P.R.China.
6. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510080, China.
*These authors made equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
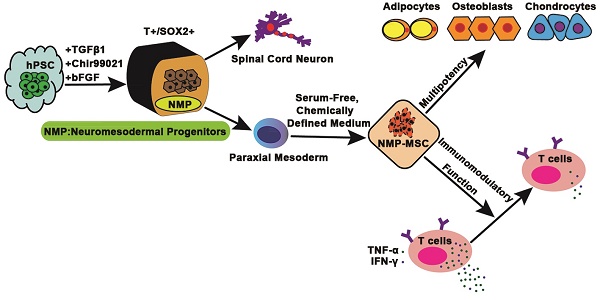
Rationale: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) hold great promise in the treatment of various diseases including autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases, etc., due to their pleiotropic properties. However, largely incongruent data were obtained from different MSC-based clinical trials, which may be partially due to functional heterogeneity among MSC. Here, we attempt to derive homogeneous mesenchymal stem cells with neuromesodermal origin from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC) and evaluate their functional properties.
Methods: Growth factors and/or small molecules were used for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC) into neuromesodermal progenitors (NMP), which were then cultured in animal component-free and serum-free induction medium for the derivation and long-term expansion of MSC. The resulted NMP-MSC were detailed characterized by analyzing their surface marker expression, proliferation, migration, multipotency, immunomodulatory activity and global gene expression profile. Moreover, the in vivo therapeutic potential of NMP-MSC was detected in a mouse model of contact hypersensitivity (CHS).
Results: We demonstrate that NMP-MSC express posterior HOX genes and exhibit characteristics similar to those of bone marrow MSC (BMSC), and NMP-MSC derived from different hPSC lines show high level of similarity in global gene expression profiles. More importantly, NMP-MSC display much stronger immunomodulatory activity than BMSC in vitro and in vivo, as revealed by decreased inflammatory cell infiltration and diminished production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in inflamed tissue of CHS models.
Conclusion: Our results identify NMP as a new source of MSC and suggest that functional and homogeneous NMP-MSC could serve as a candidate for MSC-based therapies.
Keywords: neuromesodermal progenitors, mesenchymal stem cells, human pluripotent stem cells, differentiation, immunomodulatory activity
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact