13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(6):1572-1579. doi:10.7150/thno.31986 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Polymerase Chain Reaction using “V” Shape Thermal Cycling Program
1. Natural Products Research Center, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610041, P. R. China
2. Ethnomedicine College, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chengdu 611137, P. R. China
3. College of pharmacy, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611137, P. R. China
Abstract
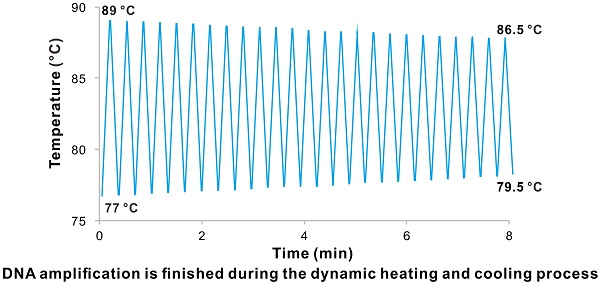
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the most commonly used technique in molecular biology and diagnostics. To achieve faster PCR reaction time, two strategies were employed by previous studies. That includes improving the thermal ramp rate by developing novel devices to reduce the time wasted on temperature transitions and cutting the holding time in every step, which could even lead to compromise in amplification efficiency. Hence the need to further improve the technique.
Methods: A different way to achieve fast DNA amplification is developed by using the previously thought wasted time spent on heating and cooling the samples to finish the amplification. That means the holding time of the three procedures are omitted and this could be carried out on the ordinary PCR thermal cyclers.
Results: 2/3 of the amplification time is easily saved, compared to the conventionally used method. Additionally, the reaction time could be further reduced by using longer primers with higher melting temperature (Tm). The record time of the “V” shape Polymerase chain reaction (VPCR) conducted on ordinary PCR machine for amplification of a 98 bp fragment is 8 min. Furthermore, VPCR still retains the merits of traditional PCR technique, including specificity, sensitivity, generality, and compatibility with quantitative detection.
Conclusion: It is confirmed that the three procedures of PCR could be completed during the dynamic heating and cooling process when the cyclers are run at a moderate thermal ramp rate. As VPCR described here is based on the current PCR system, it could be implemented in any biological Lab immediately and provide great convenience to the people working in the field of life science and human health.
Keywords: VPCR, Ordinary PCR thermal cyclers, DNA amplification finished within 8 min
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact