13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(2):405-423. doi:10.7150/thno.29832 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Delayed Remote Ischemic Preconditioning ConfersRenoprotection against Septic Acute Kidney Injury via Exosomal miR-21
1. Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University
2. Department of Nephrology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University
3. Shanghai Medical Center of Kidney
4. Shanghai Institute of Kidney and Dialysis, Shanghai, China
5. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Kidney and Blood Purification, Shanghai, China
6. Hemodialysis quality control center of Shanghai
7. Department of Cardiac Surgery, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai
8. Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, Shanghai
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
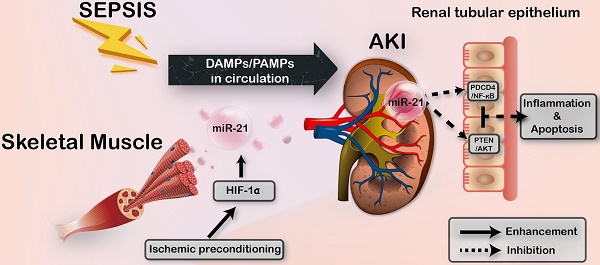
Sepsis is a common and life-threatening systemic disorder, often leading to acute injury of multiple organs. Here, we show that remote ischemic preconditioning (rIPC), elicited by brief episodes of ischemia and reperfusion in femoral arteries, provides protective effects against sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (AKI).
Methods: Limb rIPC was conducted on mice in vivo 24 h before the onset of cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), and serum exosomes derived from rIPC mice were infused into CLP-challenged recipients. In vitro, we extracted and identified exosomes from differentiated C2C12 cells (myotubes) subjected to hypoxia and reoxygenation (H/R) preconditioning, and the exosomes were administered to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated mouse tubular epithelial cells (mTECs) or intravenously injected into CLP-challenged miR-21 knockout mice for rescue experiments.
Results: Limb rIPC protected polymicrobial septic mice from multiple organ dysfunction, systemic accumulation of inflammatory cytokines and accelerated parenchymal cell apoptosis through upregulation of miR-21 in a hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α)-dependent manner in the ischemic limbs of mice. However, in miR-21 knockout mice or mice that received HIF-1α siRNA injection into hind limb muscles, the organ protection conferred by limb rIPC was abolished. Mechanistically, we discovered that miR-21 was transported from preischemic limbs to remote organs via serum exosomes. In kidneys, the enhanced exosomal miR-21 derived from cultured myotubes with H/R or the serum of mice treated with rIPC integrated into renal tubular epithelial cells and then targeted the downstream PDCD4/NF-κB and PTEN/AKT pathways, exerting anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects and consequently attenuating sepsis-induced renal injury both in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates a critical role for exosomal miR-21 in renoprotection conferred by limb rIPC against sepsis and suggests that rIPC and exosomes might serve as the possible therapeutic strategies for sepsis-induced kidney injury.
Keywords: remote ischemic preconditioning, miR-21, sepsis, acute kidney injury, exosomes
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact