13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(2):575-592. doi:10.7150/thno.21648 This issue Cite
Research Paper
circRNA Mediates Silica-Induced Macrophage Activation Via HECTD1/ZC3H12A-Dependent Ubiquitination
1. Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210009, China;
2. Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210009, China;
3. Department of Respiration, Zhongda Hospital, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210009, China;
4. Key Laboratory of Developmental Genes and Human Disease, Southeast University, Nanjing, 210096, China;
5. Nine Department of Respiratory Medicine, Nanjing Chest Hospital, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210029, China;
6. Department of Respiratory Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210029, China;
7. Department of Respiratory Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210029, China.
Abstract
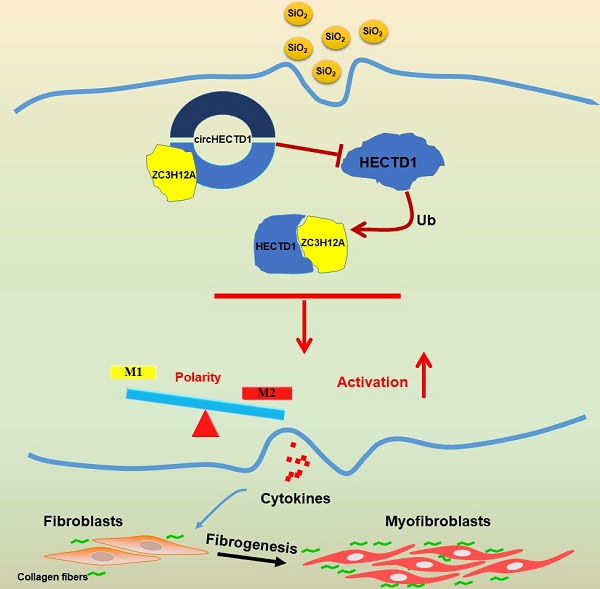
Rationale: Phagocytosis of silicon dioxide (SiO2) into lung cells causes an inflammatory cascade that results in fibroblast proliferation and migration, followed by fibrosis. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a subclass of non-coding RNAs detected within mammalian cells; however, researchers have not determined whether circRNAs are involved in the pathophysiological process of silicosis. The upstream molecular mechanisms and functional effects on cell apoptosis, proliferation and migration were investigated to elucidate the role of circRNAs in SiO2-induced inflammation in pulmonary macrophages.
Methods: Primary cultures of alveolar macrophages from healthy donors and patients as well as the RAW264.7 macrophage cell line were used to explore the functions of circHECTD1 (HECT domain E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1) in macrophage activation.
Results: The results of the experiments indicated that 1) SiO2 concomitantly decreased circHECTD1 levels and increased HECTD1 protein expression; 2) circHECTD1 and HECTD1 were involved in SiO2-induced macrophage activation via ubiquitination; and 3) SiO2-activated macrophages promoted fibroblast proliferation and migration via the circHECTD1/HECTD1 pathway. Tissue samples from silicosis patients confirmed the upregulation of HECTD1.
Conclusions: Our study elucidated a link between SiO2-induced macrophage activation and the circHECTD1/HECTD1 pathway, thereby providing new insight into the potential use of HECTD1 in the development of novel therapeutic strategies for treating silicosis.
Keywords: circHECTD1, migration, fibrosis, silicosis.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact