13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(1):237-255. doi:10.7150/thno.21945 This issue Cite
Review
Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine
1. Cancer Institute (Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Intervention, National Ministry of Education & Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Medical Sciences, Zhejiang Province), The Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310009 China;
2. Institute of Translational Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310029 China;
3. College of Basic Medical Sciences, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310058 China.
Abstract
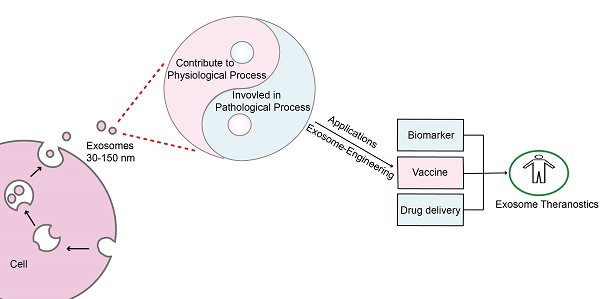
Exosomes are common membrane-bound nanovesicles that contain diverse biomolecules, such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Exosomes are derived from cells through exocytosis, are ingested by target cells, and can transfer biological signals between local or distant cells. Exosome secretion is a constitutive phenomenon that is involved in both physiological and pathological processes and determines both the exosomal surface molecules and the contents. Hence, we can exploit exosomes as biomarkers, vaccines and drug carriers and modify them rationally for therapeutic interventions. However, it is still a challenge to identify, isolate and quantify exosomes accurately, efficiently and selectively. Further studies on exosomes will explore their potential in translational medicine and provide new avenues for the creation of effective clinical diagnostics and therapeutic strategies; the use of exosomes in these applications can be called exosome theranostics. This review describes the fundamental processes of exosome formation and uptake. In addition, the physiological and pathological roles of exosomes in biology are also illustrated with a focus on how exosomes can be exploited or engineered as powerful tools in translational medicine.
Keywords: exosome, extracellular vesicle, translational medicine, biomarker, drug delivery.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact