13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(17):4301-4312. doi:10.7150/thno.21450 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Long-term Effect of Biomineralized Insulin Nanoparticles on Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
1. Center for Biomaterials and Biopathways, Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027, China;
2. Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies, Zhejiang University, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027, China;
3. Institute of Translational Medicine, Zhejiang University, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310027, China.
Abstract
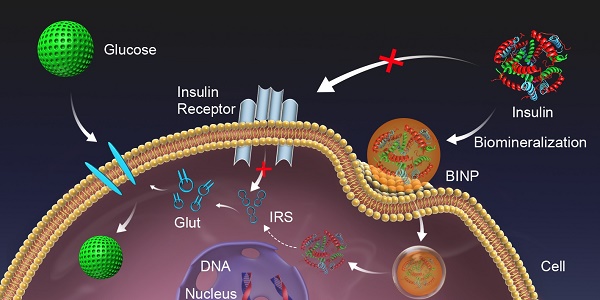
Intracellular insulin may exhibit a long-term effect in regulating protein synthesis, DNA synthesis, and gene transcription. However, the intracellular delivery of insulin is a great challenge. Here, we describe how a simple biomineralization modification of insulin can transport it into intact cells on a large scale, leading to a long-term therapeutic effect on diabetes mellitus. Using insulin-resistant HepG2 cell and diabetic KKAy mice as models, in vitro and in vivo assessments have demonstrated that biomineralized insulin nanoparticles can trigger glucose metabolism, and this improvement extends after the treatment. The potential exists to improve the current treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus through biomineralized modifications of insulin. This study provides a new paradigm of biomimetic nanotechnology for biomedical applications.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes, biomineralization, insulin, intracellular delivery.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact