13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(7):2067-2077. doi:10.7150/thno.19427 This issue Cite
Review
Current Strategies and Challenges for Purification of Cardiomyocytes Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
1. Department of Biomedical Sciences, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong;
2. Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, USA;
3. Severance Biomedical Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
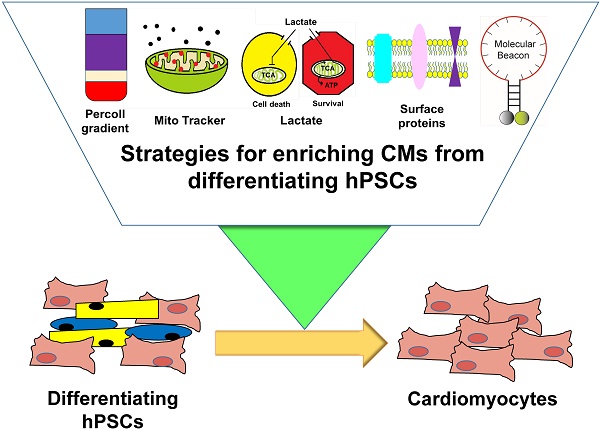
Cardiomyocytes (CMs) derived from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are considered a most promising option for cell-based cardiac repair. Hence, various protocols have been developed for differentiating hPSCs into CMs. Despite remarkable improvement in the generation of hPSC-CMs, without purification, these protocols can only generate mixed cell populations including undifferentiated hPSCs or non-CMs, which may elicit adverse outcomes. Therefore, one of the major challenges for clinical use of hPSC-CMs is the development of efficient isolation techniques that allow enrichment of hPSC-CMs. In this review, we will discuss diverse strategies that have been developed to enrich hPSC-CMs. We will describe major characteristics of individual hPSC-CM purification methods including their scientific principles, advantages, limitations, and needed improvements. Development of a comprehensive system which can enrich hPSC-CMs will be ultimately useful for cell therapy for diseased hearts, human cardiac disease modeling, cardiac toxicity screening, and cardiac tissue engineering.
Keywords: Cardiomyocytes, hPSCs
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact