13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(5):1360-1372. doi:10.7150/thno.16532 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Nucleolin-targeted Extracellular Vesicles as a Versatile Platform for Biologics Delivery to Breast Cancer
1. Institute of Biomedicine & Department of Cell Biology, Jinan University; National Engineering Research Center of Genetic Medicine; Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Bioengineering Medicine, Guangzhou, China;
2. Department of Chemistry, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
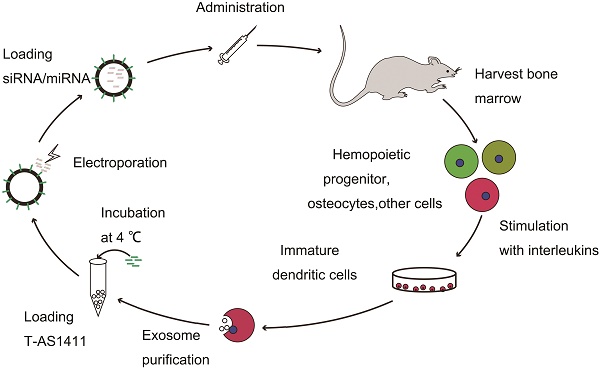
Small interfering RNAs (siRNA)/microRNAs (miRNA) have promising therapeutic potential, yet their clinical application has been hampered by the lack of appropriate delivery systems. Herein, we employed extracellular vesicles (EVs) as a targeted delivery system for small RNAs. EVs are cell-derived small vesicles that participate in cell-to-cell communication for protein and RNA delivery. We used the aptamer AS1411-modified EVs for targeted delivery of siRNA/microRNA to breast cancer tissues. Tumor targeting was facilitated via AS1411 binding to nucleolin, which is highly expressed on the surface membrane of breast cancer cells. This delivery vesicle targeted let-7 miRNA delivery to MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro as confirmed with fluorescent microscopic imaging and flow cytometry. Also, intravenously delivered AS1411-EVs loaded with miRNA let-7 labeled with the fluorescent marker, Cy5, selectively targeted tumor tissues in tumor-bearing mice and inhibited tumor growth. Importantly, the modified EVs were well tolerated and showed no evidence of nonspecific side effects or immune response. Thus, the RNAi nanoplatform is versatile and can deliver siRNA or miRNA to breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Our results suggest that the AS1411-EVs have a great potential as drug delivery vehicles to treat cancers.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles (EVs), Aptamer, Tumor-targeted delivery system, siRNA, microRNA.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact