13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(5):1164-1176. doi:10.7150/thno.17711 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Physiological Effects of Ac4ManNAz and Optimization of Metabolic Labeling for Cell Tracking
1. Predictive Model Research Center, Korea Institute of Toxicology, Daejeon, Korea,
2. Advanced Radiation Technology Institute, Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Jeonbuk, Korea,
3. Center for Theragnosis, Biomedical Research Institute, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul, Republic of Korea,
4. Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea,
5. System Toxicology Research Center, Korea Institute of Toxicology, Daejeon, Korea,
6. Department of Radiation Biotechnology and Applied Radioiostope Science, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea,
7. Department of Human and Environmental Toxicology, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
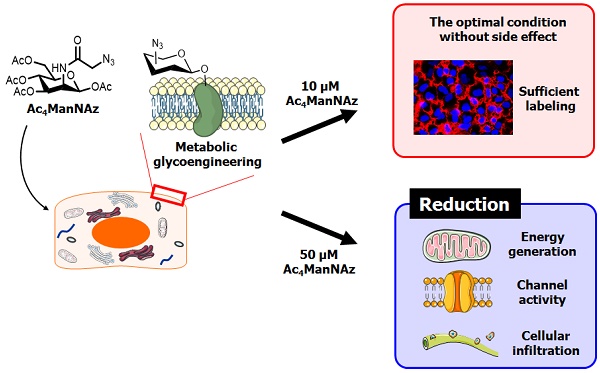
Metabolic labeling techniques are powerful tools for cell labeling, tracking and proteomic analysis. However, at present, the effects of the metabolic labeling agents on cell metabolism and physiology are not known. To address this question, in this study, we analyzed the effects of cells treated with Ac4ManNAz through microarray analysis and analyses of membrane channel activity, individual bio-physiological properties, and glycolytic flux. According to the results, treatment with 50 μM Ac4ManNAz led to the reduction of major cellular functions, including energy generation capacity, cellular infiltration ability and channel activity. Interestingly, 10 μM Ac4ManNAz showed the least effect on cellular systems and had a sufficient labeling efficiency for cell labeling, tracking and proteomic analysis. Based on our results, we suggest 10 μM as the optimum concentration of Ac4ManNAz for in vivo cell labeling and tracking. Additionally, we expect that our approach could be used for cell-based therapy for monitoring the efficacy of molecule delivery and the fate of recipient cells.
Keywords: Metabolic labeling, Azido-sugar, Modified glycosylation, Azido group, Physiology
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact