13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(2):377-389. doi:10.7150/thno.16627 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Anti-angiogenic Nanotherapy Inhibits Airway Remodeling and Hyper-responsiveness of Dust Mite Triggered Asthma in the Brown Norway Rat
1. Department of Medicine, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA
2. Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
3. Philips Research Laboratories, Hamburg, Germany
Received 2016-6-28; Accepted 2016-10-4; Published 2017-1-1
Abstract
Although angiogenesis is a hallmark feature of asthmatic inflammatory responses, therapeutic anti-angiogenesis interventions have received little attention. Objective: Assess the effectiveness of anti-angiogenic Sn2 lipase-labile prodrugs delivered via αvβ3-micellar nanotherapy to suppress microvascular expansion, bronchial remodeling, and airway hyper-responsiveness in Brown Norway rats exposed to serial house dust mite (HDM) inhalation challenges. Results: Anti-neovascular effectiveness of αvβ3-mixed micelles incorporating docetaxel-prodrug (Dxtl-PD) or fumagillin-prodrug (Fum-PD) were shown to robustly suppress neovascular expansion (p<0.01) in the upper airways/bronchi of HDM rats using simultaneous 19F/1H MR neovascular imaging, which was corroborated by adjunctive fluorescent microscopy. Micelles without a drug payload (αvβ3-No-Drug) served as a carrier-only control. Morphometric measurements of HDM rat airway size (perimeter) and vessel number at 21d revealed classic vascular expansion in control rats but less vascularity (p<0.001) after the anti-angiogenic nanotherapies. CD31 RNA expression independently corroborated the decrease in airway microvasculature. Methacholine (MCh) induced respiratory system resistance (Rrs) was high in the HDM rats receiving αvβ3-No-Drug micelles while αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles markedly and equivalently attenuated airway hyper-responsiveness and improved airway compliance. Total inflammatory BAL cells among HDM challenged rats did not differ with treatment, but αvβ3+ macrophages/monocytes were significantly reduced by both nanotherapies (p<0.001), most notably by the αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles. Additionally, αvβ3-Dxtl-PD decreased BAL eosinophil and αvβ3+ CD45+ leukocytes relative to αvβ3-No-Drug micelles, whereas αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles did not. Conclusion: These results demonstrate the potential of targeted anti-angiogenesis nanotherapy to ameliorate the inflammatory hallmarks of asthma in a clinically relevant rodent model.
Keywords: Asthma, Nanomedicine, Prodrug, Angiogenesis, Fluorine MRI, Respiratory function
Introduction
Asthmatic symptoms like bronchial hyper-responsiveness and overall reduced lung function reflect the underlying structural changes to the airway wall due to chronic inflammation.[1] Among the notable structural remodeling features of asthmatic airways is the long-recognized expansion of the bronchial vascular bed. Earlier research showed that alterations in bronchial blood flow or capacity in asthmatic patients were quantitatively reflected as changes in airway temperature. These changes in airway temperature were unrelated to cardiac output or pulmonary blood flow, suggesting that they were associated with vascular expansion within the bronchial circulation. [2-6] Systemic vascular expansion in the lung is associated with macrophage activation, elaborating pro-angiogenic chemokines that stimulate neovascular expansion. [7, 8]
Anti-inflammatory systemic or inhaled corticosteroids are critical therapeutic drugs used in the acute and chronic management of asthma patients, which at higher doses elicit pleiotropic pharmacologic vascular remodeling effects including local vasoconstriction and inhibition of the production of pro-angiogenic cytokines and chemokines. [9-12] Neovastat, an anti-inflammatory marine cartilage derivative, suppressed airway inflammation associated with reductions in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α) expression in murine lung tissue in ovalbumin-sensitized mice. [13] Despite the close interrelationship of airway inflammation and increased microvascularity, anti-angiogenesis treatment, such as anti-VEGF therapy, has not been considered, perhaps because such blockades can be circumvented by alternative pro-angiogenic factors and endothelial signaling pathways.
Fumagillin is a highly potent anti-angiogenic mycotoxin that inhibits methionine aminopeptidase-2 in proliferating endothelial cells leading to apoptosis.[14, 15] In its stabilized water soluble form, designated TNP-470, it had anecdotal benefit in cancer patients but at the systemic doses required patients experienced mild to moderate neurocognitive side-effects. [16-21] Native fumagillin incorporated into the lipid encapsulated αvβ3-targeted nanoparticles markedly lowered the effective dose in preclinical cancer [22] and rheumatoid arthritis [23] models, which was further reduced when included as an Sn2 lipase labile phospholipid prodrug. [24, 25]
Paclitaxel, which interacts with tubulin also has anti-angiogenic benefit. [26] However, the off-target adverse profile of taxanes precludes their general systemic use as an anti-angiogenic therapeutic for asthma. Unlike native fumagillin, hydrophobic taxanes were not effectively retained in lipid encapsulated αvβ3-targeted nanoparticles during circulation except when modified into an Sn2 lipase labile prodrug. [27] Importantly, at an effective anti-angiogenic drug level of taxane administered as αvβ3-targeted Sn2 docetaxel prodrug nanoparticles in the Vx2 rabbit cancer model, Abraxane dosed iv was ineffective. [27]
In the present study, lipase labile phospholipid prodrug forms of fumagillin (Fum-PD) or docetaxel (Dxtl-PD) were incorporated into lipid-based micelles for targeted drug delivery in the context of asthma to determine if anti-angiogenesis nanotherapy could offer a new therapeutic approach to this serious disease. [25, 27-29] In general, lipase labile prodrugs inactivate chemotherapeutic compounds and prevent premature drug-loss from the nanoparticle during circulation. Sensitive functional groups of drugs are sequestered within the hydrophobic acyl membrane compartment and protected from the surrounding water milieu. [30] Lipid prodrugs are delivered by a mechanism termed “contact-facilitated drug delivery” (CFDD). [31] For CFDD the targeted cell surface receptor, e.g., αvβ3, is used as a “mooring” that allows the lipid nanoparticle surface to form an irreversible hemifusion complex with the target cell membrane. [32, 33] The prodrugs transfer spontaneously into the target cell outer and then inner membranes. The continuity of the inner cell membrane with intracellular membranes, except mitochondria, distributes the prodrugs throughout the cellular compartments. Within the cell a myriad of intracellular lipases can cleave the Sn2 ester of the lipid backbone, liberating and reactivating the compound within the cytosol. Direct targeting of proliferating neoendothelial cells with αvβ3-targeted Fum-PD or Dxtl-PD nanoparticles induces apoptosis. [24]
In this proof of concept study, the impact of anti-neovascular therapy was evaluated as a therapeutic regimen for asthma in a clinically relevant animal model. The temporal and spatial distribution of angiogenesis, vascularity, and airway reactivity in a Brown Norway rat model following serial allergen challenges with house dust mite (HDM) was recently characterized by Wagner et al. [34] Utilizing this model, the overarching objectives of this proof-of-concept study were: 1) to confirm the anti-angiogenic efficacy in asthma of αvβ3-targeted Fum-PD or Dxtl-PD micelles using MR simultaneous dual 19F/1H neovascular molecular imaging (3T); 2) to assess the impact of anti-angiogenesis therapy on airway hyper-reactivity and compliance response to methacholine challenge; 3) to delineate the impact of anti-angiogenesis treatment on airway vascular morphology and structural remodeling; and 4) to characterize the treatment effects on bronchial alveolar lavage cell numbers and type.
Methods
Preparation of Sn2 lipase labile fumagillin prodrug
A modified synthesis of the Sn2 prodrug was developed and accomplished in two steps [29]: 1) saponifying fumagillin dicyclohexylamine salt to fumagillol, and 2) esterifying the product with 1-palmitoyl-2-azelaoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (PAzPC).[29] (Figure 1A) Briefly, fumagillin dicyclohexylamine salt (NCI) in 0.1N NaOH was stirred at ambient temperature (4h). The reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl ether (3X) and dried with anhydrous Na2SO4. After filtering the Na2SO4 the ether was evaporated to a yellow oil (yield ~60%). The final structure of fumagillol was confirmed by MS.
A solution of 1-hexadecyl-2-azelaoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (Paz-PC, Avanti Polar Lipids) 1mM, 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP)(5X) and N,N'-dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide (DCC) (5X) was added to 1mM fumagillol in minimal dry chloroform. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight at ambient temperature then passed over a short pad of silica gel using EtOAc/n-hexane (1:1). The filtered solvent was removed in vacuo, and the oil residue was purified by column chromatography on SiO2 using EtOAc/n-hexane for elution to yield the fumagillol prodrug (Fum-PD) compound as a pale yellowish solid (yield: 54%). Mass spectroscopy (MS) confirmed the final synthetic structure: m/z [C49H88NO13P, calculated mass= 929.60, observed= 930].
Preparation of Sn2 lipase labile docetaxel prodrug
For the present research modified synthesis of docetaxel prodrug was developed. Docetaxel (Sigma Aldrich) dissolved in dimethylformamide (DMF) 0.02 mmole/ml was combined with Paz-PC in chloroform (0.02 mmole/ml) then carbodiimide (DCC) / dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) on silica was added. The mixture was incubated at room temperature overnight then filtered. The DMF was dried in vacuo to a solid. (Figure 1B) The compound was isolated and purified by preparative thin layer chromatography (prep-TLC) (50% yield) and the structure confirmed by NMR and ESI MS spectroscopy (Dxtl-PD: m/z [C76H115N2O23P, calculated mass=1454.76, observed M+H+=1456]).
ανβ3-integrin antagonist homing ligand
The ανβ3-integrin antagonist was a quinalone nonpeptide developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging (US patent 6,511,648 and related patents) and provided coupled to phosphatidylethanolamine through a polyethylene glycol2000 spacer (ανβ3-PEG-PE, Kereos, Inc., Figure 1C). The antagonist was initially characterized as the 111In-DOTA conjugate RP478 and cyan 5.5 homologue TA145.[35] PFC nanoparticles present ~300 ligands/particle with an IC50 of 50 pM for the Mn2+-activated αvβ3-integrin. [36]
The homing high specificity of ανβ3-nanoparticles (>150 nm nominal diameter) was previously characterized using microscopic histology of Matrigel™ plugs implanted into Rag1tm1Mom Tg (Tie-2-lacZ)182-Sato and C57Bl/6 mice [37], using photoacoustic molecular imaging of neovascular sprouting in a Matrigel™ plug model in rats [38], and in an ischemic left pulmonary artery ligation (LPAL) model of bronchial angiogenesis induction in rodents. [39] Robust reproducibility of serial targeting and MR molecular imaging within individual rabbits bearing Vx2 tumors over approximately one week was also reported. [40]
Synthesis of αvβ3-integrin targeted therapeutic micelles
Therapeutic mixed micelles were prepared by microfluidization using 20% (v/v) polysorbate 80 (NOF America), 2.0% (w/v) of a surfactant co-mixture, and 1.7% (w/v) glycerin suspension in carbonate buffer (pH 6.5). The surfactant co-mixture of nanoparticles included: 97.8 mole% lecithin and 0.2 mole% of αvβ3-PEG-PE, and 2 mole% of Fum-PD or Dxtl-PD. Drug concentrations of the therapeutic micelles were equimolar (0.5mM). AlexaFluor™ or rhodamine dyes for fluorescent microscopy were coupled to PEG2000-PE lipid anchors (0.6 mole%) and included in the surfactant co-mixture at the equimolar expense of lecithin for fluorescent microscopy. “No-Drug” nanoparticles excluded the 2 mole% of Fum-PD or Dxtl-PD, which was replaced by lecithin. Surfactant components were combined with the polysorbate, buffer, and glycerin with pH adjusted to 6.5, and the mixtures were homogenized at 20,000 psi for 4 minutes. The micelles were preserved under inert gas in sterile sealed vials until use.
Synthesis of αvβ3-integrin targeted perfluorocarbon nanoparticles for MR imaging
Phospholipids-encapsulated perfluorocarbon (PFC) nanoparticles (NP) for neovascular MR molecular imaging were prepared as a microfluidized suspension of 20% (v/v) perfluoroctylbromide (PFOB, Exfluor Inc., Round Rock, TX), 2.0% (w/v) of a surfactant co-mixture, and 1.7% (w/v) glycerin in pH 6.5 carbonate buffer as described above. The surfactant co-mixture of nanoparticles included: ~ 99.8 mole% lecithin and 0.2 mole% of αvβ3-PEG-PE. Dyes, e.g. AlexaFluor™ or rhodamine, were coupled to PEG2000-PE lipid anchors (0.6 mole%) and included in the surfactant co-mixture at the equimolar expense of lecithin for fluorescent microscopy. Typical particle size determined by dynamic light scattering was 214 ± 20 nm with a polydispersity index of 0.15 ± 0.5 and zeta potential, (ζ) of 23 ± 12 mV (Brookhaven ZetaPlus, Brookhaven Instruments Corporation).
MR neovascular imaging response to αvβ3-targeted Fum-PD and Dxtl-PD nanotherapy
Male Brown Norway rats (BN, Charles River, 100 g) were administered house dust mite allergen (HDM, Der p 1; 100 μg/100µl challenge, Greer Laboratories) by intranasal inspiration, as previously reported [34] on days 0, 5 and 7 followed by i.v. αvβ3-No-Drug (n=6), αvβ3-Fum-PD (n=6) or αvβ3-Dxtl-PD (n=6) on days 6 and 8 (35µl, 0.7 µmole/kg/dose to offset anticipated transbiliary losses in rodents). [41] All animals were studied using simultaneous dual 19F/1H MR neovascular imaging at 3T (Achieva 3T, Philips Healthcare, Andover, MA). Animal protocols were approved by the Johns Hopkins and Washington University Animal Care and Use Committees.
On day 10, 2 days following the last anti-angiogenesis nanotherapy, all HDM treatment groups were administered αvβ3-PFOB NPs (35µl) via tail vein catheter. Two hours later, the animals were anesthetized with a non-fluorinated anesthetic (ketamine/xylazine; 85/13 mg/kg) and imaged with high-resolution simultaneous 19F/1H MRI using an in-house custom dual-tuned solenoid transmit-receive coil. Simultaneous 3D 19F/1H imaging was used employing a novel steady state ultra-short echo time (UTE) technique (TE/TR=0.1ms/1.96ms) with the frequencies set to the resonance of 1H and the CF2 groups of the PFOB spectrum (offset 6328Hz from 19F; representing 12 of 17 total 19F nuclei). [42-45] Using a highly oversampled 3D radial readout scheme, a series of 19F images were reconstructed, post facto, by modifying the Nyquist weighting factor applied to samples in k-space. A Nyquist value that provided the optimal balance between the 19F signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and image resolution was selected and that value was uniformly applied to each individual animal[46]. 1H images were used at the original resolution of 1.25x1.25x1.25 mm3. In this anesthetized rat model, neither mathematical correction nor respiratory gating were required to adjust for motion, as the breathing motion was of the same order of magnitude or less than the pixel resolution and any related ghosting was averaged out over the 28 min total scan time.
19F/1H MR image analysis
MR data sets were imported into ImageJ (NIH) for quantification of the 19F signal. The method for measuring neovascularity was based upon the integral of 19F signal intensity from αvβ3-PFOB NPs. Lung regions of interest (ROIs) were defined from anatomical matching of multi-slice 1H and 19F MR datasets. These ROIs consistently included the heart in order to capture neovascularity located proximate to the trachea. To determine the background noise level, these same (size and shape) ROIs were repositioned in the upper left area of the image, devoid of any signal or potential respiratory-related ghosting. For each 19F 2D image slice, the average signal in this background ROI was calculated and subtracted from the image to standardize. Small experiment-to-experiment differences in absolute image intensity due to variations in RF coil tuning or animal position were referenced to a PFOB emulsion standard placed with the field of view adjacent to the animal. The normalized lung 19F signal was then averaged across all lung ROI slices.
Microscopic imaging to corroborate MR neovascular imaging
In a separate cohort (n=3/treatment) treated identically to those animals used for 19F/1H MR molecular imaging, animals were euthanized 2 hours after injection of fluorescent αvβ3-PFOB NPs. Lungs were inflated to a pressure of 12 cmH2O and infused with warmed liquefied 1% agarose (42ºC). The upper airway, major bronchi, and surrounding tissue were resected and snap frozen in optimum cutting temperature (OCT) compound. Tissues were sectioned and fluorescent microscopic images (40x) were obtained with an Olympus BX61 microscope. Cell nuclei were stained blue with DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, dihydrochloride).
Pharmacokinetics of αvβ3-micelles in naive and HDM challenged Brown Norway rats
Male BN rats (100 g; n=6) were administered house dust mite allergen or PBS control by intranasal instillation on days 0, 5 and 7. On day 8, αvβ3-micelles, incorporating 2 mole% Gd-DTPA-bisoleate as a trace marker in the surfactant commixture, were injected via tail vein. Serial blood samples were drawn for pharmacokinetic analysis 0, 5, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90 and 120 minutes post dose. Blood samples were analyzed for gadolinium using ICP OES (Optima 8000, Perkin-Elmer). The results were fit to a two compartmental model (Gd3+ concentration = A e-αt + B e-βt; GraphPad Prism 5.04).
Pathological response to anti-angiogenesis nanotherapy in asthmatic Brown Norway rats
Using the sensitization protocol previously discussed [34], separate cohorts of male BN rats (BN, 125-150 g) were given HDM allergen by intranasal instillation twice/week for 3 wks. Following the second HDM treatment each week, rats received αvβ3-No-Drug, αvβ3-Fum-PD (1.0 µmole/kg/dose), or αvβ3-Dxtl-PD (50µl, 1.0 µmole/kg/dose) by tail vein injection (n=4 rats/group). Rats were studied one day after the last intranasal challenge of HDM.
For these animals, lungs were inflated with Z-fix (Anatech, Battle Creek, MI) to a pressure of 12 cmH2O for 24 hr. The left lung was divided into three sections, embedded in paraffin, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Airways (all cut in cross-section; max/min diameter ratio <1.5) were sized by basement membrane perimeter (ImageJ, NIH) and the number of blood vessels within the associated airway wall was enumerated. Morphometry was determined in lung sections from rats given αvβ3-No-Drug, αvβ3-Fum-PD, or αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles (n=4 rats/group).
Airway smooth muscle responsiveness following anti-angiogenesis nanotherapy
Following the same HDM and micelle dosing regimen, male BN rats (n=6/treatment group) received αvβ3-No-Drug, αvβ3-Fum-PD, or αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles 1 day after the second weekly HDM instillation. After 3 weeks the rats were anesthetized (ketamine /xylazine, 75/5 mg/kg), intubated, and paralyzed (0.6 mg succinylcholine chloride) and dynamic respiratory mechanics were determined. Animals were ventilated (90 breaths/min; 8 ml/kg) and lung resistance and compliance were measured (Scireq Flexivent). Following the baseline measurements, cumulative dose-response relationships to methacholine chloride (MCh) aerosol (15 sec with an Aeroneb nebulizer) at challenges of 0 (PBS vehicle), 0.1, 1.0, 3.0, and 5 mg/ml MCh were obtained.
RT-PCR of endothelial specific genes following anti-angiogenesis nanotherapy
Based on previous findings and according to the same procedures [34], CD31, an endothelial-related gene, was evaluated in large airways of HDM exposed rats given αvβ3-No-Drug (n=3), αvβ3-Fum-PD (n=4), or αvβ3-Dxtl-PD (n=4) micelles. Total RNA was isolated from homogenized tracheal tissue (RNeasy;Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's protocol, cDNA was generated with QuantiTect Reverse Transcription kit (Qiagen; Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad) settings and primers were as previously reported. [34]
Bronchoalveolar lavage recovery and cytospin preparation
Immediately after death, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was performed using three aliquots of warm (37oC) saline (2 ml / aliquot, 0.9% NaCl) delivered to the right lung and then gently aspirated (3-4 rats per treatment group). One ml of the recovered volume was separated and the cells were measured using a hemocytometer. Total cell numbers were back-calculated. BAL cells (5 x104) were spun onto glass slides by cyto-centrifugation, fixed and stained with HEMA 3 STAT PACK kit (Fisher Scientific, Kalamazoo, MI). The cytospin slides were differentiated by standard cytological procedures.
FACS staining and flow cytometry of bronchoalveolar lavage cells
BAL fluid was withdrawn as described above and immediately centrifuged (1400 rpm, 5 min, 4°C). The cell pellet was resuspended in PBS for FACS staining. Dead cells were excluded using VIVID® (Invitrogen). Cells were blocked with anti-rat CD32 (BD Pharmingen) and subjected to biotinylated anti-αvβ3 (eBioscience). Subsequent surface staining was performed using FITC anti-rat CD11c, Pacific Blue anti-rat CD11b (Bio-Rad), APC anti-rat ED-9 (eBioscience), PE anti-rat MHC II (Santa Cruz) and APC/Cy7 anti-rat CD45 (Biolegend). Cells were acquired on a BD FACSAria (BD Biosciences) and data were analyzed with FlowJo software (Tree Star, Ashland, OR).
Statistics
Imaging data were statistically analyzed using SAS (SAS Institute Inc.) using general linear models, including ANOVA and ANOCOV employing Tukey's test for multiple comparisons for significant F-statistics. Group replication was powered to detect a 50% or greater difference at an alpha level of 0.05 with a beta power of 0.80. [47] Least-squares regression was used to estimate the slopes of airway size (perimeter, mm) versus vessel number within treatment groups. Airway morphology data were analyzed with two-way ANOVA controlling for the within animal variability using Fisher's LSD for mean separation. Means with a probability of difference ≤ 0.05 were accepted as significant. All nominal data are presented as the mean ± the standard error of the mean.
Results
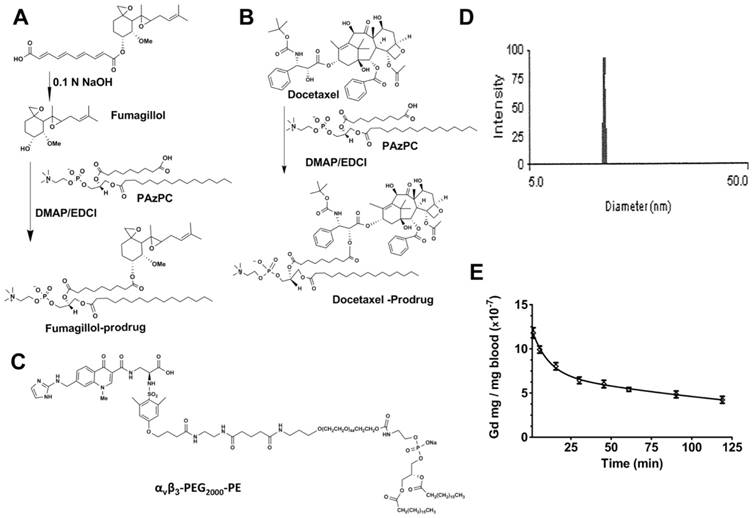
Fum-PD and Dxtl-PD were synthesized by modification of prior procedures as described in the Methods section and illustrated schematically in Figure 1A,B, respectively. The αvβ3-peptidomimetic homing ligand utilized was provided as a gift (Kereos, Inc, St. Louis). (Figure 1C) αvβ3-mixed micelles used for drug delivery had nominal particle sizes of 16 ± 4 nm and polydispersities between 0.1 and 0.2 based on dynamic light scattering (DLS) and an electrophoretic potential (ζ) of -20 ± 6 mV, across batches. Figure 1D presents a representative DLS distribution example for an αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelle formulation. Pharmacokinetics of the αvβ3-micelles tagged with a gadolinium-lipid tracer was studied in HDM (n=3) and naïve rats (n=3) with no difference (p>0.05) appreciated between the two groups. The results fit to a two compartmental model (Gd3+ concentration = A e-αt + B e-βt) were in very close agreement and were pooled to provide alpha distribution half-life of 6.9 min and a beta elimination half-life of 154.6 min estimates; the beta elimination rate unexpectedly exceeded the sampling regimen. (Figure 1E)
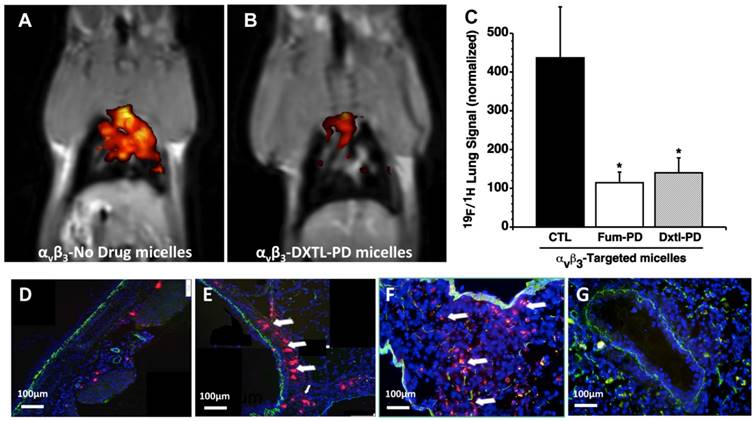
The early induction of bronchial neovascularization after ischemic left pulmonary artery ligation and HDM sensitization was previously validated and characterized using 19F/1H MR molecular imaging and corroborating histopathology and functional airway studies. [34, 39] Anti-angiogenesis treatment of the asthmatic HDM rats with αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles markedly and equally reduced (p<0.01) airway neovascular MR signal when compared to asthmatic animals receiving αvβ3-No-Drug micelles. (Figure 2A-C) The binding of the fluorescent αvβ3- perfluorooctylbromide nanoparticles (αvβ3-PFOB-NP) within the bronchus of an HDM rat following αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles nanotherapy versus the dense accumulation of αvβ3-PFOB-NP along the large airway following αvβ3-No-Drug micelles was readily differentiated. (Figure 2 D, E) Qualitatively the previously reported 19F signal intensities of non-asthmatic control rats were similar to the control 19F imaging data in the present study. [34]
Anti-angiogenic MR molecular imaging results were corroborated by immunofluorescence microscopy. The sparse binding of the red fluorescent αvβ3-PFOB-NP within the bronchus of an HDM rat following αvβ3-Fum-PD micelle nanotherapy versus the dense accumulation of αvβ3-PFOB-NP along the large airway following αvβ3-No-Drug micelles was easily differentiated. (Figure 2 D, E) Red fluorescent αvβ3-micelles accumulated within the HDM inflamed bronchus and surrounding parenchyma, whereas these particles administered to naïve rats (i.e., no HDM treatment) had negligible binding within or around the large pulmonary airways or vasculature. (Figure 2F,G) Collectively, the results corroborate the tomographic changes observed with 19F/1H MR neovascular imaging with αvβ3-PFOB NP and showed that integrin-targeted Fum-PD or Dxtl-PD micelles effectively diminished angiogenesis in HDM rats.
A. Scheme 1 Synthesis of fumagillin (fumagillol) PAz-PC prodrug. B. Scheme 2 Synthesis of docetaxel prodrug. C. Structure αvβ3-peptidomimetic-PEG2000-PE. D. Example of dynamic light scattering micelle particle size distribution (αvβ3-Dxtl-PD). E. Averaged pharmacokinetic profile of αvβ3-micelles containing a Gd3+-lipid marker in the surfactant commixture. The two compartment model Gd3+ concentration (C) = A e-αt + B e-βt revealed an alpha distribution half-life of 6.9 min and a beta elimination half-life of 154.6 min.
A, B. 19F/1H MR molecular following anti-angiogenesis treatment in HDM rats with αvβ3-Dxtl-PD (right) revealed markedly reduced airway neovascular MR signal when compared to the control asthmatic animals receiving αvβ3-No-Drug micelles (left). C. Histogram of 19F/1H MR tomographic molecular imaging results showing equivalent reduction in neovascularity with anti-angiogenesis micelles (P<0.01). D. Sparse binding of the red fluorescent αvβ3-PFOB NPs within the bronchus of an HDM rat following αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles nanotherapy. E. Heavy accumulation of red fluorescent αvβ3-PFOB NPs along the large airway following αvβ3-No-Drug micelles. F. Red fluorescent αvβ3-micelles accumulated heavily within the HDM inflamed bronchus and surrounding parenchyma. G. Red fluorescent αvβ3-micelles administered to naïve rats (i.e., no HDM treatment) had negligible nonspecific binding. Green autofluorescence was noted in the airway and vascular walls.
Progressive HDM inhalation over three weeks in the Brown Norway rats was previously associated with increased (p<0.05) airway vascularity measurable with microscopy. [34] Gross airway and vascular casts demonstrated increased vascularity in HDM compared to control (PBS) rats after 3 wks of sensitization. In that study, 3 wks of HDM sensitization elicited an abundance of blood vessels within the airway wall compared to a paucity of bronchial vessels observed in the control bronchi. Striking differences in the influx of inflammatory cells, airway wall thickening, and smooth muscle contraction were noted in the HDM rats relative to the PBS controls. Further, the correlation slopes of airway size (perimeter, mm) versus the number of vessels normalized for airway area were different between HDM and PBS rats (p=0.002) and reflected increased numbers of vessels in HDM rats compared to PBS rats over an equivalent size range of airways studied (0.5-3mm).
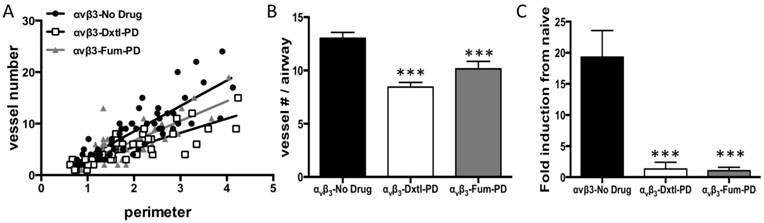
These asthmatic changes were recapitulated at three weeks in the present study. The anti-angiogenic impact of serial αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles after HDM inhalation demonstrated by MRI on day 10 was associated with profound attenuation of airway vascularity at 21 days. Least-squares regression slopes of airway size (perimeter, mm) versus vessel number significantly differed among treatment groups (p<0.001). Control HDM rats had more vessels as revealed by the slope (4.9 ± 0.5) than those receiving αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles (2.7 ± 0.3) or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles (3.8 ± 0.5), (p<0.001). Further, the regression slope of αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelle response was lower than the αvβ3-Fum-PD micelle observation. (p=0.0394). (Figure 3A) After normalizing vessel number for airway size (i.e., diameter), both αvβ3-Dxtl-PD (p<0.001; n=41 airways) and αvβ3-Fum-PD (p<0.001; n=45 airways) micelles decreased vascularity to a similar extent relative to the HDM rats receiving αvβ3-No-Drug micelles (n=55 airways). (Figure 3B)
The marked morphometric vascular changes were corroborated by examining the RNA expression of endothelial-specific genes in tracheal tissue. The tracheal expression of CD31, a common biomarker of nascent and mature endothelial cells, was determined and compared to naïve tissue expression levels. (Figure 3C) CD31 expression was markedly decreased in large airway tissue after αvβ3-Dxtl-PD and αvβ3-Fum-PD micelle treatment compared to the HDM rats given αvβ3-No-Drug micelles (p<0.001).
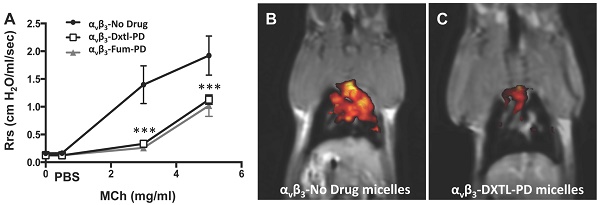
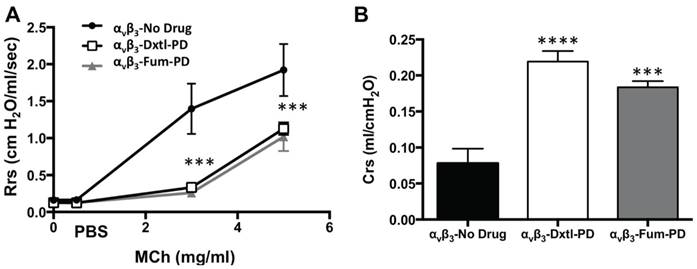
Lung functional changes, a clinical hallmark of asthma, were assessed in a separate cohort of HDM rats that received αvβ3-Dxtl-PD, αvβ3-Fum-PD or αvβ3-No-Drug micelles. Respiratory system resistance (Rrs) was measured after increasing methacholine (MCh) concentrations in each group. (Figure 4A) Airway reactivity to MCh was markedly attenuated among rats treated with αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles compared with HDM rats receiving αvβ3-No-Drug particles (p<0.001), which was equivalent to the resistance response reported for naive rats previously. MCh airway responsiveness did not differ between the αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD nanotherapies. Respiratory system compliance (Crs) in HDM rats following the 3mg MCh challenge was greater after the anti-angiogenic nanotherapies than in the αvβ3-No-Drug micelle group (p<0.001) (Figure 4B). Airway smooth muscle thickening correlates with response to MCh, but additional morphological measurements were not obtained to reconfirm this relationship in this study.
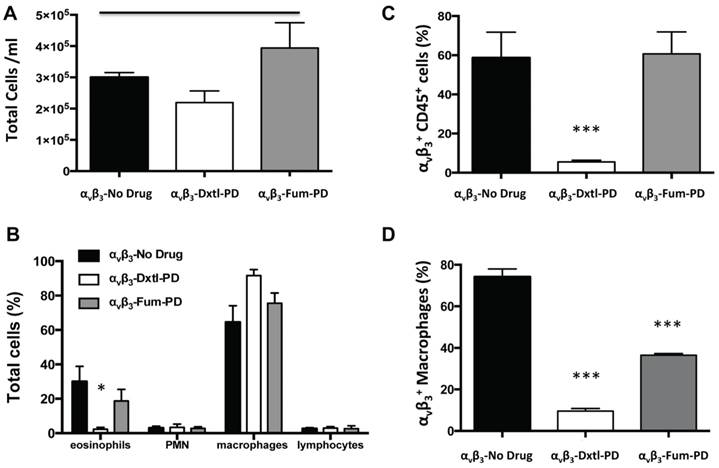
Bronchoalveolar (BAL) cell profiles were compared among HDM rats receiving αvβ3-No-Drug micelles versus the αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelle treatments. Total inflammatory cells recovered were similar (p>0.05) between the groups at 3 weeks. (Figure 5A) BAL cell differential profiles among animals receiving αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles had a lower (p<0.05) percentage of eosinophils compared to HDM rats receiving αvβ3-Fum-PD or αvβ3-No-Drug treatments. (Figure 5B) Further, αvβ3-Dxtl-PD nanotherapy decreased αvβ3+ CD45+ leukocytes (p<0.001) whereas αvβ3-Fum-PD and αvβ3-No-Drug treatments had no effect. (Figure 5C) BAL flow cytometry showed that both αvβ3-Fum-PD and αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelle treatments decreased (p<0.001) αvβ3+ macrophage/monocyte numbers versus the control micelles (Figure 5D).
A. Least-squares regression slopes of airway size (perimeter, mm) versus vessel number significantly differed among treatment groups (p<0.001). Control HDM (●) rats receiving αvβ3-No-Drug had more blood vessels as revealed by the slope (4.9 ± 0.5) than those receiving αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles (2.7 ± 0.3, ◻) or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles (3.8 ± 0.5, ▲), (p<0.001). Further, the regression slope of αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelle response was lower than the αvβ3-Fum-PD micelle observation. (p=0.0394). B. After normalizing vessel number for airway size (i.e., diameter), both αvβ3-Dxtl-PD (p<0.0001) and αvβ3-Fum-PD (p<0.0003) micelles decreased vascularity to a similar extent relative to the HDM rats receiving αvβ3-No-Drug micelles (n=4 rats/group; 2-way ANOVA and Fisher's LSD). C. CD31 expression in the trachea of the three treatment groups compared to naïve tissue. Gene expression for CD31, a common endothelial cell marker, was markedly decreased in large airway tissue (trachea) after αvβ3-Dxtl-PD and αvβ3-Fum-PD compared to αvβ3-No-Drug (p=0.0005).
Pulmonary functional changes in HDM rats receiving αvβ3-Dxtl-PD, αvβ3-Fum-PD or αvβ3-No-Drug micelles. A. Respiratory system resistance (Rrs) was measured after increasing methacholine (MCh) concentrations showing markedly attenuated reactivity among rats treated with αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles. (*** p <0.001). B. Respiratory system compliance (Crs) in HDM rats following the 3mg MCh challenge showing greater compliance after the anti-angiogenic nanotherapies.
Bronchoalveolar (BAL) cell profiles. A. Total inflammatory cells recovered were similar between the groups at 3 weeks. B. BAL cell differential profiles showed a lower (p<0.05) percentage of eosinophils (EOS) in HDM rats receiving αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelle than αvβ3-Fum-PD or αvβ3-No-Drug treatments. C. αvβ3-Dxtl-PD nanotherapy decreased αvβ3+ CD45+ leukocytes (p<0.001) whereas αvβ3-Fum-PD and αvβ3-No-Drug treatments had no effects. D. BAL flow cytometry revealing that αvβ3-Fum-PD and αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelle treatments decreased (p<0.001) αvβ3+ macrophage/monocyte numbers versus the control micelles (αvβ3-Dxtl-PD > αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles).
Discussion
Structural remodeling of asthmatic airways has long been associated with microvascular expansion of the capillary bed. Although angiogenesis is a hallmark feature of asthmatic inflammatory responses, specific therapeutic anti-angiogenesis interventions have not been considered. In the present studies, anti-angiogenic prodrug therapeutics delivered by a micelle therapy markedly suppressed microvascularity, bronchial remodeling, and airway hyper-responsiveness in HDM rats, suggesting for the first time that direct anti-neovascular therapy can contribute significantly to asthma management.
The bioactivity and effectiveness of Sn2 lipase labile prodrugs of Dxtl and Fum delivered via αvβ3-integrin targeted micelles in HDM rats was definitively demonstrated noninvasively with 19F/1H MR neovascular molecular imaging using vascular-constrained αvβ3-PFOB nanoparticles and a clinical 3T scanner. The spatial and temporal character of neovascular expansion within the upper airways/bronchi of the HDM rats given αvβ3-No-Drug micelles recapitulated the 19F/1H MR response previously reported at this field strength. [34] However, the neovascular signal among rats receiving αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles or αvβ3-Fum-PD was greatly reduced, validating that the prodrugs retained drug bioactivity and that αvβ3-micelles effectively homed and bound to the neovasculature. These 19F/1H MR imaging results were corroborated by immunofluorescent microscopic studies that also delineated the differential targeting of fluorescent αvβ3-PFOB nanoparticles (red) in HDM rats receiving αvβ3-No-Drug and αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles. The targeting of fluorescent αvβ3-micelles (red) into the airway wall and local surrounding tissue in No-Drug treated HDM rats but not in naïve animals is congruent with the therapeutic effects measured.
Within this study, MR provided early recognition of HDM induced airway inflammation as reflected by neovascular expansion and provided a quantitative read-out of anti-angiogenic treatment response. In the broader context, this result and previous reports of clinical 19F/1H MR molecular imaging of the lung pose the prospect for more detailed and quantitative image guided management of asthma patients, particularly those with moderate to severe disease. The workhorse imaging modality of lung imaging is computed tomography (CT) and for cancer is positron emission tomography/CT (PET/CT). As healthcare costs associated with newer biological precision medicine therapies soar for patients with moderate and particularly severe asthma, improved high-sensitivity noninvasive nonionizing imaging to optimize and minimize the use of these therapies will be welcome. [48-51] Anticipating that repeat imaging studies will be used in pediatric patients as well as adults, the implementation of MRI techniques becomes highly attractive and circumvents potential cumulative X-ray risks.
Increased vascular density in the sub-epithelial submucosa of the lungs of asthmatic patients as well as other bronchial vasculature abnormalities is well documented and associated with increased blood flow and edematous airway thickening. [52] After 3 weeks of biweekly HDM challenges, morphometric measurements of airway size (perimeter) and vessel number revealed classic asthma-related vascular expansion in the HDM rats receiving αvβ3-No-Drug micelles. HDM rats given the anti-angiogenic αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelle therapies had dramatically less microvascularity, which was confirmed by reduced CD31 RNA expression in these animals compared to the αvβ3-No-Drug controls.
Increased vascularization was previously correlated with airflow limitation and bronchial hyper-responsiveness. [12, 53, 54] In the present study, MCh induced respiratory system resistance (Rrs) was high in the HDM rats receiving the αvβ3-No-Drug particles but markedly and equivalently attenuated among rats treated with αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles. Similarly, respiratory system compliance (Crs) was increased among HDM rats exposed to anti-angiogenic prodrug nanotherapy compared with the No-Drug micelles. Clearly, the relationship between airway hyper-responsiveness and vascularity observed in patients was observed in the HDM rat model, and by extension the substantial improvements elicited by αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles in HDM rats could reasonably translate into patients.
As expected, microscopic examination revealed marked increases in inflammatory cells in HDM rat airways and surrounding tissues that were not appreciated in the lungs from control animals. Increased αvβ3-integrin expression heavily co-localized with activated macrophages by microscopy was also appreciated in BAL cells of control HDM. However, αvβ3+ macrophages were significantly reduced by both targeted nanotherapies and significantly more so by the αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelle treatment. Anti-angiogenic therapy is typically viewed from the perspective of neovasculature pruning, but recent studies intensively examining the effects of αvβ3-Fum-PD in inflammatory mouse models have shown that direct anti-angiogenesis therapy is also anti-inflammatory. [24]
Fumagillin is well known to impact the proliferation of neovascular endothelial cells, but this mycotoxin has negligible effects on non-endothelial cell types. [55] The overall outcome of a series of detailed experiments to delineate the potential mechanism for local inflammation suppression with integrin-targeted fumagillin determined that endothelial nitric oxide (NO) derived and released from the drug-targeted neoendothelial cells modulated local macrophage inflammatory response through AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). NO-induced AMPK activation decreased the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activity and increased autophagic flux, as evidenced by p62 depletion and increased autolysosome formation. Increased macrophage autophagy flux was associated with degradation of IkappaB kinase (IKK), suppression of the NF-ĸB-p65 signaling pathway, and ultimately decreased inflammatory cytokine release. [24] Thus, the anti-inflammatory impact of Fum-PD was indirectly mediated through the endothelial NO release with suppressive feedback on the local macrophages.
αvβ3-micelles, similar in size to IgG antibodies, penetrate into inflamed tissue readily. These micelles can home and bind to extravascular targets [56], including macrophages expressing activated αvβ3-integrin. Fum-PD is ineffective when co-incubated with activated macrophages in culture, but it is effective against vascular tubule formation in vitro. [24, 57] Dxtl-PD can suppress macrophage inflammatory cytokine release in vitro and in vivo, as well as being anti-angiogenic [30] (Supporting Information: S1). In the present study, αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles, in addition to the anti-angiogenic anti-inflammatory effects elicited by targeting neoendothelial cells similar to αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles, they likely bound phagocytic cells, possibly the M2 phenotype macrophages increased in antigen-induced asthma. Of note in breast cancer, M2 macrophages uniquely express activated αvβ3-integrin. [58]
αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles but not αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles reduced BAL αvβ3+ CD45+ cells, probably as a direct consequence of targeted taxane prodrug delivery. This would be expected due to the endothelial cellular specificity of fumagillin. BAL eosinophils were generally elevated in the HDM rats, but markedly reduced among animals receiving αvβ3-Dxtl-PD micelles and not the αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles. Since αvβ3-integrin expression by eosinophils is uncommon, we hypothesize that the reduction of eosinophils was related to αvβ3-Dxtl-PD impacting M2 macrophages within a complex Th1/Th2-macrophage-eosinophil cross-talk network. [59-61] Further delineation of these complex interrelationships is beyond the scope of this initial study.
While the present report has shown for the first time that targeted αvβ3-micelle nanotherapy can ameliorate bronchial airway hyper-reactivity and inflammatory characteristics of dust-mite induced asthma in rats, specific mechanistic studies will be required to deconvolve the disruption of the complex roles of cellular inflammatory components and chemokines involved in the pathologic remodeling within the inflamed airways. Further, these data demonstrate that HDM induced asthma can be approached in a nontraditional therapeutic fashion, additional research to optimize the pharmacology and to elucidate the safety of this targeted therapeutic micelle approach is warranted.
Conclusion
The results of this study clearly indicate that direct anti-angiogenesis therapy with αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles can ameliorate asthma in the house dust mite triggered Brown Norway rat model. Airway hyper-responsiveness and increased microvascularity, classic hallmarks of asthma, were significantly reduced with these treatments. Whereas the dogma of efficacy surrounding anti-angiogenesis therapy has been associated with the impact of vascular pruning, in the current study αvβ3-Dxtl-PD or αvβ3-Fum-PD micelles treatment of proliferating neoendothelial cells led to secondary anti-inflammatory benefits.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Information S1.
Abbreviations
3D: three dimensional
αvβ3: alpha v beta 3 integrin
AMPK: adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase
ANOVA: analysis of variance
ANOCOV: analysis of covariance
APC: allophycocyanin
BAL: bronchoalveolar lavage
CD11b: cluster of differentiation 11 - antigen on monocytes/macrophages and microglia
CD45: cluster of differentiation 11 - lymphocyte common antigen
CD31: cluster of differentiation 31 - Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM)
CD32: cluster of differentiation 32 - Fc gamma receptor on B-cells
CFDD: contact-facilitated drug delivery
Crs: respiratory system compliance
CT: computed tomography
Cy7: cyanine7 - near infrared fluorescent dye
DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
DCC: carbodiimide
DMAP: dimethylaminopyridine
DMF: dimethylformamide
DOTA: tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid
DTPA: diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid
Dxtl-PD: docetaxel-prodrug
ESI: electrospray ionization
FACS: fluorescence-activated cell sorting
FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate
FOV: field of view
Fum-PD: fumagillin-prodrug
HDM: house dust mites
HIF-2α: hypoxia-inducible factor-2α
ICP-OES: inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry
IKK: IkappaB kinase
MCh: Methacholine
MR: magnetic resonance
MS: mass spectroscopy
mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin
NCI: National Cancer Institute
NF-ĸB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell
NFkB-p65: a subunit of NF-kappa-B transcription complex
NMR: nuclear magnetic resonance
NO: nitric oxide
OCT: optimum cutting temperature
p62: nucleoporin p62 is a protein complex associated with the nuclear envelope
PAzPC: palmitoyl-2-azelaoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
PBS: phosphate buffered saline
PE: phosphatidylethanolamine
PEG: polyethylene glycol
PET/CT: positron emission tomography/CT
PFOB: perfluorooctylbromine
psi: pounds per square inch
RF: radio frequency
RNA: ribonucleic acid
ROI: regions of interest
Rrs: respiratory system resistance
Sn2: stereospecific numbering-by convention the hydroxyl group of the second carbon of glycerol
T: Tesla
TE: echo time
TR: repetition time
TNP-470: synthetic analog of fumagillin
UTE: ultra-short echo time
VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in whole or part by grants from the NIH HL113392 (GML/EMW), CA154737 (GML), HL125838 (BR), HL122471 (GML), HL112518 (GML), and HHSN26820140042C (GML). We appreciate the further support provided Samuel A Wickline M.D. and the Barnes-Jewish Research Foundation.
Competing Interests
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
References
1. Keglowich LF, Borger P. The three A's in asthma - airway smooth muscle, airway remodeling & angiogenesis. Open Respir Med J. 2015;9:70-80
2. Gilbert IA, Winslow CJ, Lenner KA, Nelson JA, McFadden Jr ER. Vascular volume expansion and thermally induced asthma. Eur Respir J. 1993;6:189-97
3. McFadden Jr ER. Microvasculature and airway responses. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;145:S42-S3
4. Gilbert IA, Regnard J, Lenner KA, Nelson JA, McFadden Jr ER. Intrathoracic airstream temperatures during acute expansions of thoracic blood volume. Clin Sci. 1991;81:655-61
5. Gilbert IA, Fouke JM, McFadden Jr ER. Intra-airway thermodynamics during exercise and hyperventilation in asthmatics. J Appl Physiol. 1988;64:2167-74
6. Deal Jr EC, McFadden Jr ER, Ingram Jr RH. Hyperpnea and heat flux: Initial reaction sequence in exercise-induced asthma. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;46:476-83
7. Mitzner W, Lee W, Georgakopoulos D, Wagner E. Angiogenesis in the mouse lung. Am J Pathol. 2000;157:93-101
8. D'Alessio FR, Zhong Q, Jenkins J, Moldobaeva A, Wagner EM. Lung angiogenesis requires CD4(+) forkhead homeobox protein-3(+) regulatory T cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;52:603-10
9. Chetta A, Zanini A, Foresi A, Del Donno M, Castagnaro A, D'Ippolito R. et al. Vascular component of airway remodeling in asthma is reduced by high dose of fluticasone. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:751-7
10. Feltis BN, Wignarajah D, Reid DW, Ward C, Harding R, Walters EH. Effects of inhaled fluticasone on angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor in asthma. Thorax. 2007;62:314-9
11. Hoshino M, Takahashi M, Takai Y, Sim J, Aoike N. Inhaled corticosteroids decrease vascularity of the bronchial mucosa in patients with asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001;31:722-30
12. Orsida BE, Li X, Hickey B, Thien F, Wilson JW, Walters EH. Vascularity in asthmatic airways: relation to inhaled steroid dose. Thorax. 1999;54:289-95
13. Lee SY, Chung SM. Neovastat (AE-941) inhibits the airway inflammation via VEGF and HIF-2 alpha suppression. Vascul Pharmacol. 2007;47:313-8
14. Liu S, Widom J, Kemp CW, Crews CM, Clardy J. Structure of human methionine aminopeptidase-2 complexed with fumagillin. Science. 1998;282:1324-7
15. Sin N, Meng L, Wang MQ, Wen JJ, Bornmann WG, Crews CM. The anti-angiogenic agent fumagillin covalently binds and inhibits the methionine aminopeptidase, MetAP-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:6099-103
16. Ahmed MH, Konno H, Nahar L, Tanaka T, Naito Y, Nakamura S. et al. The angiogenesis inhibitor TNP-470 (AGM-1470) improves long-term survival of rats with liver metastasis. J Surg Res. 1996;64:35-41
17. Konno H, Tanaka T, Kanai T, Maruyama K, Nakamura S, Baba S. Efficacy of an angiogenesis inhibitor, TNP-470, in xenotransplanted human colorectal cancer with high metastatic potential. Cancer. 1996;77:1736-40
18. Shusterman S, Grupp SA, Barr R, Carpentieri D, Zhao H, Maris JM. The angiogenesis inhibitor TNP-470 effectively inhibits human neuroblastoma xenograft growth, especially in the setting of subclinical disease. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:977-84
19. Bhargava P, Marshall JL, Rizvi N, Dahut W, Yoe J, Figuera M. et al. A Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of TNP-470 administered weekly to patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:1989-95
20. Kudelka AP, Verschraegen CF, Loyer E. Complete remission of metastatic cervical cancer with the angiogenesis inhibitor TNP-470. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:991-2
21. Offodile R, Walton T, Lee M, Stiles A, Nguyen M. Regression of metastatic breast cancer in a patient treated with the anti-angiogenic drug TNP-470. Tumori. 1999;85:51-3
22. Winter PM, Caruthers SD, Kassner A, Harris TD, Chinen LK, Allen JS. et al. Molecular imaging of angiogenesis in nascent Vx-2 rabbit tumors using a novel alpha(nu)beta3-targeted nanoparticle and 1.5 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5838-43
23. Zhou HF, Chan HW, Wickline SA, Lanza GM, Pham CT. Alpha v beta 3-targeted nanotherapy suppresses inflammatory arthritis in mice. FASEB J. 2009;23:2978-85
24. Zhou HF, Yan H, Hu Y, Springer LE, Yang X, Wickline SA. et al. Fumagillin prodrug nanotherapy suppresses macrophage inflammatory response via endothelial nitric oxide. ACS Nano. 2014;8:7305-17
25. Zhou HF, Yan H, Senpan A, Wickline SA, Pan D, Lanza GM. et al. Suppression of inflammation in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis using targeted lipase-labile fumagillin prodrug nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2012;33:8632-40
26. Bocci G, Di Paolo A, Danesi R. The pharmacological bases of the antiangiogenic activity of paclitaxel. Angiogenesis. 2013;16:481-92
27. Pan D, Schmieder AH, Wang K, Yang X, Senpan A, Cui G. et al. Anti-angiogenesis therapy in the Vx2 rabbit cancer model with a lipase-cleavable Sn 2 taxane phospholipid prodrug using alpha(v)beta(3)-targeted theranostic nanoparticles. Theranostics. 2014;4:565-78
28. Zhang R, Pan D, Cai X, Yang X, Senpan A, Allen JS. et al. Alpha nu beta 3-targeted copper nanoparticles incorporating an Sn 2 lipase-labile fumagillin prodrug for photoacoustic neovascular imaging and treatment. Theranostics. 2015;5:124-33
29. Pan D, Sanyal N, Schmieder AH, Senpan A, Kim B, Yang X. et al. Antiangiogenic nanotherapy with lipase-labile Sn-2 fumagillin prodrug. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012;7:1507-19
30. Pan D, Pham CT, Weilbaecher KN, Tomasson MH, Wickline SA, Lanza GM. Contact-facilitated drug delivery with Sn2 lipase labile prodrugs optimize targeted lipid nanoparticle drug delivery. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2016;8:85-106
31. Lanza GM, Yu X, Winter PM, Abendschein DR, Karukstis KK, Scott MJ. et al. Targeted antiproliferative drug delivery to vascular smooth muscle cells with a magnetic resonance imaging nanoparticle contrast agent: implications for rational therapy of restenosis. Circulation. 2002;106:2842-7
32. Partlow K, Lanza G, Wickline S. Exploiting lipid raft transport with membrane targeted nanoparticles: A strategy for cytosolic drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2008;29:3367-75
33. Soman N, Lanza G, Heuser J, Schlesinger P, Wickline S. Synthesis and characterization of stable fluorocarbon nanostructures as drug delivery vehicles for cytolytic peptides. Nano Lett. 2008;8:1131-6
34. Wagner EM, Jenkins J, Schmieder A, Eldridge L, Zhang Q, Moldobaeva A. et al. Angiogenesis and airway reactivity in asthmatic Brown Norway rats. Angiogenesis. 2015;18:1-11
35. Meoli DF, Sadeghi MM, Krassilnikova S, Bourke BN, Giordano FJ, Dione DP. et al. Noninvasive imaging of myocardial angiogenesis following experimental myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 2004;113:1684-91
36. Schmieder AH, Caruthers SD, Zhang H, Williams TA, Robertson JD, Wickline SA. et al. Three-dimensional MR mapping of angiogenesis with {alpha}5{beta}1({alpha}{nu}{beta}3)-targeted theranostic nanoparticles in the MDA-MB-435 xenograft mouse model. FASEB J. 2008;22:4179-89
37. Pan D, Pramanik M, Senpan A, Allen JS, Zhang H, Wickline SA. et al. Molecular photoacoustic imaging of angiogenesis with integrin-targeted gold nanobeacons. FASEB J. 2011;25:875-82
38. Khlebtsov N, Dykman L. Biodistribution and toxicity of engineered gold nanoparticles: a review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:1647-71
39. Schmieder AH, Wang K, Zhang H, Senpan A, Pan D, Keupp J. et al. Characterization of early neovascular response to acute lung ischemia using simultaneous 19F/1H MR molecular imaging. Angiogenesis. 2014;17:51-60
40. Schmieder AH, Winter PM, Williams TA, Allen JS, Hu G, Zhang H. et al. Molecular MR imaging of neovascular progression in the Vx2 tumor with alpha v beta 3-targeted paramagnetic nanoparticles. Radiology. 2013;268:470-80
41. Bulte JWM, Schmieder AH, Keupp J, Caruthers SD, Wickline SA, Lanza GM. MR cholangiography demonstrates unsuspected rapid biliary clearance of nanoparticles in rodents: Implications for clinical translation. Nanomedicine. 2014;10:1385-8
42. Keupp J, Caruthers S, Rahmer J, Williams T, Wickline S, Lanza G. et al. Fluorine-19 MR molecular imaging of angiogenesis on Vx-2 tumors in rabbits using ανβ3-targeted nanoparticles. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med. 2009:223
43. Keupp J, Rahmer J, Grässlin I, Mazurkewitz P, Schaeffter T, Lanza G. et al. Simultaneous dual-nuclei imaging for motion corrected detection and quantification of 19F imaging agents. Magn Reson Med. 2011;66:1116-1122
44. Rahmer J, Keupp J, Caruthers S, Lips O, Williams T, Wickline S. et al. Dual resolution simultaneous 19F/1H in vivo imaging of targeted nanoparticles. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med. 2009:611
45. Rahmer J, Keupp J, Caruthers S, Lips O, Williams T, Wickline S. et al. 19F/1H Simultaneous 3D radial imaging of atherosclerotic rabbits using self-navigated respiratory motion compensation. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med. 2009:4611
46. Caruthers SD, Keupp J, Rahmer J, Lanza GM, Wickline SA. Multi-resolution simultaneous 19F/1H 3D radial imaging for self-navigated respiratory motion-corrected and quantitative imaging. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2010;12(Suppl 1):O56
47. Cochran W, Cox G. Experimental Designs. Second ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons. 1957
48. López Tiro JJ, Contreras EAC, del Pozo MER, Vera JG, Linnemann DL. Real life study of three years omalizumab in patients with difficult-to-control asthma. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2015;43:120-6
49. Giovannini-Chami L, Albertini M, Scheinmann P, de Blic J. New insights into the treatment of severe asthma in children. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2015;16:167-73
50. Papierniak ES, Lowenthal DT, Harman E. Novel therapies in asthma: Leukotriene antagonists, biologic agents, and beyond. A J Ther. 2013;20:79-103
51. Caruso M, Crisafulli E, Demma S, Holgate S, Polosa R. Disabling inflammatory pathways with biologics and resulting clinical outcomes in severe asthma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13:393-402
52. Dunnill MS. The pathology of asthma, with special reference to changes in the bronchial mucosa. J Clin Pathol. 1960;13:27-33
53. Vrugt B, Wilson S, Bron A, Holgate ST, Djukanovic R, Aalbers R. Bronchial angiogenesis in severe glucocorticoid-dependent asthma. Eur Respir J. 2000;15:1014-21
54. Li X, Wilson JW. Increased vascularity of the bronchial mucosa in mild asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156:229-33
55. Bernier SG, Lazarus DD, Clark E, Doyle B, Labenski MT, Thompson CD. et al. A methionine aminopeptidase-2 inhibitor, PPI-2458, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:10768-73
56. Soodgupta D, Pan D, Cui G, Senpan A, Yang X, Lu L. et al. Small molecule MYC inhibitor conjugated to integrin-targeted nanoparticles extends survival in a mouse model of disseminated multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14:1286-94
57. Esser AK, Schmieder AH, Ross MH, Xiang J, Su X, Cui G. et al. Dual-therapy with alpha v beta 3-targeted Sn2 lipase-labile fumagillin-prodrug nanoparticles and zoledronic acid in the Vx2 rabbit tumor model. Nanomedicine. 2016;12:201-11
58. Su X, Esser AK, Amend SR, Xiang J, Xu Y, Ross MH. et al. Antagonizing integrin beta3 increases immunosuppression in cancer. Cancer Res. 2016;76:3484-95
59. Jiang Z, Zhu L. Update on the role of alternatively activated macrophages in asthma. Journal of asthma and allergy. 2016;9:101-7
60. Balhara J, Gounni AS. The alveolar macrophages in asthma: a double-edged sword. Mucosal Immunol. 2012;5:605-9
61. Chung S, Lee TJ, Reader BF, Kim JY, Lee YG, Park GY. et al. FoxO1 regulates allergic asthmatic inflammation through regulating polarization of the macrophage inflammatory phenotype. Oncotarget. 2016;7:17532-46
Author contact
![]() Corresponding author: Gregory Lanza MD PhD, Professor of Medicine and Bioengineering, Oliver M. Langenberg Distinguished Professor of the Science and Practice of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Washington University Medical School, CORTEX building, Suite 101, 4320 Forest Park Ave, Saint Louis, MO. greg.lanzacom; Tel: 314-454-8813; Fax: 314-454-5265
Corresponding author: Gregory Lanza MD PhD, Professor of Medicine and Bioengineering, Oliver M. Langenberg Distinguished Professor of the Science and Practice of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Washington University Medical School, CORTEX building, Suite 101, 4320 Forest Park Ave, Saint Louis, MO. greg.lanzacom; Tel: 314-454-8813; Fax: 314-454-5265
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact