13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(8):1232-1243. doi:10.7150/thno.14409 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Adaptive and Acquired Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors Converge on the MAPK Pathway
1. State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes, Renji-Med X Clinical Stem Cell Research Center, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China;
2. Department of thoracic surgery, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China;
3. Department of Respiratory Medicine, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China;
4. Department of Pathology, the affiliated hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China;
5. Bio-X Institute, Key Laboratory for the Genetics of Developmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Ministry of Education, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China;
6. Department of Pharmacology and Chemical Biology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China;
7. Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Translational Medicine, Shanghai, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
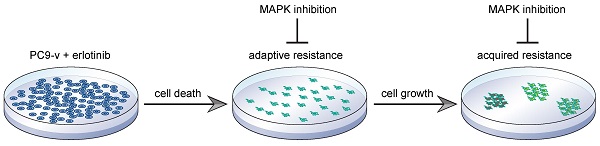
Both adaptive and acquired resistance significantly limits the efficacy of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitors. However, the distinct or common mechanisms of adaptive and acquired resistance have not been fully characterized. Here, through systematic modeling of erlotinib resistance in lung cancer, we found that feedback reactivation of MAPK signaling following erlotinib treatment, which was dependent on the MET receptor, contributed to the adaptive resistance of EGFR inhibitors. Interestingly, acquired resistance to erlotinib was also associated with the MAPK pathway activation as a result of CRAF or NRAS amplification. Consequently, combined inhibition of EGFR and MAPK impeded the development of both adaptive and acquired resistance. These observations demonstrate that adaptive and acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors can converge on the same pathway and credential cotargeting EGFR and MAPK as a promising therapeutic approach in EGFR mutant tumors.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR, MAPK
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact