13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(5):1426-1452. doi:10.7150/thno.31683 This issue Cite
Review
Evaluation of Polymer Nanoformulations in Hepatoma Therapy by Established Rodent Models
1. Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, P. R. China
2. Key Laboratory of Polymer Ecomaterials, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130022, P. R. China
3. Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, P. R. China
4. Jilin Biomedical Polymers Engineering Laboratory, Changchun 130022, P. R. China
5. Department of Gastrointestinal Colorectal and Anal Surgery, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130033, P. R. China
Abstract
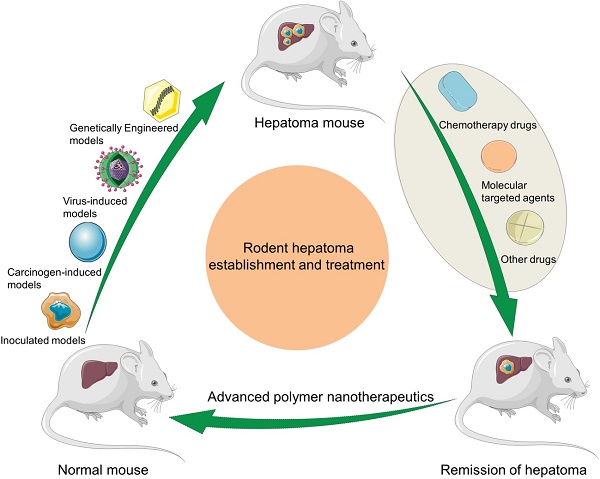
Hepatoma is one of the most severe malignancies usually with poor prognosis, and many patients are insensitive to the existing therapeutic agents, including the drugs for chemotherapy and molecular targeted therapy. Currently, researchers are committed to developing the advanced formulations with controlled drug delivery to improve the efficacy of hepatoma therapy. Numerous inoculated, induced, and genetically engineered hepatoma rodent models are now available for formulation screening. However, animal models of hepatoma cannot accurately represent human hepatoma in terms of histological characteristics, metastatic pathways, and post-treatment responses. Therefore, advanced animal hepatoma models with comparable pathogenesis and pathological features are in urgent need in the further studies. Moreover, the development of nanomedicines has renewed hope for chemotherapy and molecular targeted therapy of advanced hepatoma. As one kind of advanced formulations, the polymer-based nanoformulated drugs have many advantages over the traditional ones, such as improved tumor selectivity and treatment efficacy, and reduced systemic side effects. In this article, the construction of rodent hepatoma model and much information about the current development of polymer nanomedicines were reviewed in order to provide a basis for the development of advanced formulations with clinical therapeutic potential for hepatoma.
Keywords: hepatoma, rodent model, polymer nanoparticle, drug delivery, chemotherapy, molecular targeted therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact