13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(5):1336-1347. doi:10.7150/thno.31806 This issue Cite
Review
The Search for an Alternative to [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TATE in Neuroendocrine Tumor Theranostics: Current State of 18F-labeled Somatostatin Analog Development
1. Ahmanson Translational Imaging Division, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095
2. Department of Molecular & Medical Pharmacology, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095
3. Crump Institute for Molecular Imaging, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095
Abstract
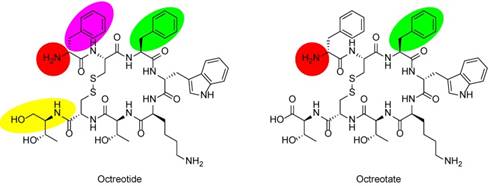
The trend to inform personalized molecular radiotherapy with molecular imaging diagnostics, a concept referred to as theranostics, has transformed the field of nuclear medicine in recent years. The development of theranostic pairs comprising somatostatin receptor (SSTR)-targeting nuclear imaging probes and therapeutic agents for the treatment of patients with neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) has been a driving force behind this development. With the Neuroendocrine Tumor Therapy (NETTER-1) phase 3 trial reporting encouraging results in the treatment of well-differentiated, metastatic midgut NETs, peptide radioligand therapy (RLT) with the 177Lu-labeled somatostatin analog (SSA) [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE is now anticipated to become the standard of care. On the diagnostics side, the field is currently dominated by 68Ga-labeled SSAs for the molecular imaging of NETs with positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT). PET/CT imaging with SSAs such as [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TATE, [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TOC, and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-NOC allows for NET staging with high accuracy and is used to qualify patients for RLT. Driven by the demand for PET/CT imaging of NETs, a commercial kit for the production of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TATE (NETSPOT) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The synthesis of 68Ga-labeled SSAs from a 68Ge/68Ga-generator is straightforward and allows for a decentralized production, but there are economic and logistic difficulties associated with these approaches that warrant the search for a viable, generator-independent alternative. The clinical introduction of an 18F-labeled SSTR-imaging probe can help mitigate the shortcomings of the generator-based synthesis approach, but despite extensive research efforts, none of the proposed 18F-labeled SSAs has been translated past prospective first-in-humans studies so far. Here, we review the current state of probe-development from a translational viewpoint and make a case for a clinically viable, 18F-labeled alternative to the current standard [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-TATE.
Keywords: neuroendocrine tumors, SSTR2, 18F-Labeling, PET imaging
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact