13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(14):3415-3431. doi:10.7150/thno.20861 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Brusatol-Mediated Inhibition of c-Myc Increases HIF-1α Degradation and Causes Cell Death in Colorectal Cancer under Hypoxia
1. Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon 22212, Republic of Korea;
2. Hypoxia-related Disease Research Center, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon 22212, Republic of Korea;
3. Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon 22212, Republic of Korea;
4. Department of Molecular Medicine, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon 22212, Republic of Korea.
* E.-T. Oh and C.W. Kim contributed equally to this article
Abstract
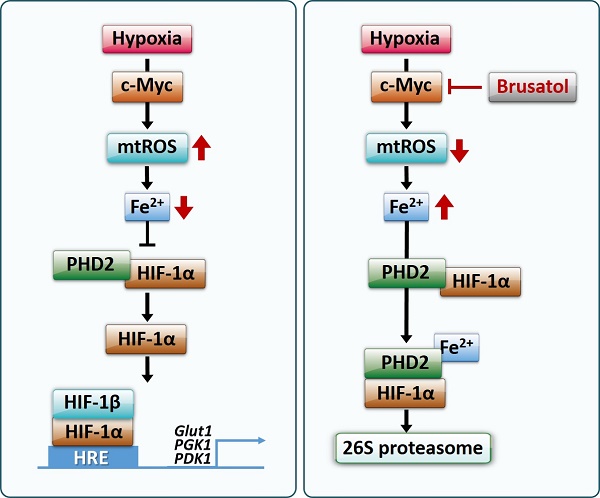
HIF-1 (hypoxia-inducible factor-1) regulates the expression of ~100 genes involved in angiogenesis, metastasis, tumor growth, chemoresistance and radioresistance, underscoring the growing interest in targeting HIF-1 for cancer control. In the present study, we investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying brusatol-induced HIF-1α degradation and cell death in colorectal cancer under hypoxia (0.5% O2). Under hypoxia, pretreatment of cancer cells with brusatol increased HIF-1α degradation and cancer cell death in a dose-dependent manner. This effect was mediated by activation of prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs), as evidenced by the block of brusatol-induced HIF-1α degradation and cancer cell death by both pharmacological inhibition and siRNA-mediated knockdown of PHDs. In addition, a ferrous iron chelator (2,2'-bypyridyl) blocked brusatol-induced degradation of HIF-1α and cancer cell death in hypoxia by inhibiting PHD activation. We further found that brusatol inhibited c-Myc expression, and showed that overexpression of c-Myc prevented brusatol-induced degradation of HIF-1α and cancer cell death by increasing mitochondrial ROS production and subsequent ROS-mediated transition of ferrous iron to ferric iron. Consistent with these results, treatment of tumor-bearing mice with brusatol significantly suppressed tumor growth by promoting PHD-mediated HIF-1α degradation. Collectively, our results suggest that brusatol-mediated inhibition of c-Myc/ROS signaling pathway increases HIF-1α degradation by promoting PHD activity and induces cell death in colorectal cancer under hypoxia
Keywords: Brusatol, Cell death, Colorectal cancer, HIF-1α, Hypoxia.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact