13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2015; 5(12):1328-1342. doi:10.7150/thno.11432 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Salmonella typhimurium Suppresses Tumor Growth via the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-1β
1. Laboratory of In Vivo Molecular Imaging, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hwasun Hospital, Gwangju, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Microbiology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Republic of Korea
3. School of Life Sciences, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), 261 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712, Republic of Korea
4. Academy of Immunology and Microbiology (AIM), Institute of Basic Science (IBS), Pohang, Republic of Korea
5. Fraunhofer IZI, Leipzig, Germany
6. Division of Integrative Biosciences and Biotechnology (IBB), Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, 790-784, Republic of Korea
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
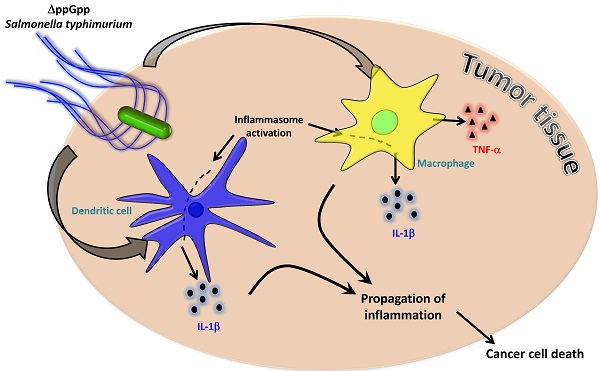
Although strains of attenuated Salmonella typhimurium and wild-type Escherichia coli show similar tumor-targeting capacities, only S. typhimurium significantly suppresses tumor growth in mice. The aim of the present study was to examine bacteria-mediated immune responses by conducting comparative analyses of the cytokine profiles and immune cell populations within tumor tissues colonized by E. coli or attenuated Salmonellae. CT26 tumor-bearing mice were treated with two different bacterial strains: S. typhimurium defective in ppGpp synthesis (ΔppGpp Salmonellae) or wild-type E. coli MG1655. Cytokine profiles and immune cell populations in tumor tissue colonized by these two bacterial strains were examined at two time points based on the pattern of tumor growth after ΔppGpp Salmonellae treatment: 1) when tumor growth was suppressed ('suppression stage') and 2) when they began to re-grow ('re-growing stage'). The levels of IL-1β and TNF-α were markedly increased in tumors colonized by ΔppGpp Salmonellae. This increase was associated with tumor regression; the levels of both IL-1β and TNF-α returned to normal level when the tumors started to re-grow. To identify the immune cells primarily responsible for Salmonellae-mediated tumor suppression, we examined the major cell types that produce IL-1β and TNF-α. We found that macrophages and dendritic cells were the main producers of TNF-α and IL-1β. Inhibiting IL-1β production in Salmonellae-treated mice restored tumor growth, whereas tumor growth was suppressed for longer by local administration of recombinant IL-1β or TNF-α in conjunction with Salmonella therapy. These findings suggested that IL-1β and TNF-α play important roles in Salmonella-mediated cancer therapy. A better understanding of host immune responses in Salmonella therapy may increase the success of a given drug, particularly when various strategies are combined with bacteriotherapy.
Keywords: Bacteria-mediated cancer therapy, Salmonella typhimurium, E. coli, IL-1β, TNF-α, dendritic cells
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact