13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(8):2209-2223. doi:10.7150/thno.30726 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Myeloid cell-derived LL-37 promotes lung cancer growth by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shanghai Tongji Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200065, China.
2. Department of Thoracic-cardiovascular Surgery, Tongji hospital,Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200065, China.
3. Department of Pharmacy, Putuo People's Hospital, Shanghai 200060, China.
4. Dairy and Functional Foods Research Unit, Eastern Regional Research Center, Agriculture Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture, Wyndmoor, PA 19038, USA.
5. Sol Sherry Thrombosis Research Center, Temple University, Philadelphia, PA 19140, USA.
6. Department of Internal Medicine V-Pulmonology, Allergology, Respiratory Intensive Care Medicine, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg 66424, Germany.
*The authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
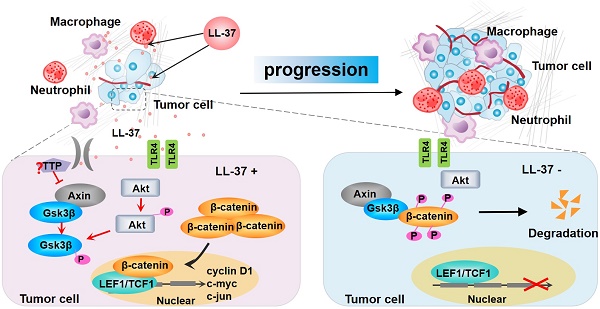
Rationale: Antimicrobial peptides, such as cathelicidin LL-37/hCAP-18, are important effectors of the innate immune system with direct antibacterial activity. In addition, LL-37 is involved in the regulation of tumor cell growth. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the functions of LL-37 in promoting lung cancer are not fully understood.
Methods: The expression of LL-37 in the tissues and sera of patients with non-small cell lung cancer was determined through immunohistological, immunofluorescence analysis, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The animal model of wild-type and Cramp knockout mice was employed to evaluate the tumorigenic effect of LL-37 in non-small cell lung cancer. The mechanism of LL-37 involving in the promotion of lung tumor growth was evaluated via microarray analyses, recombinant protein treatment approaches in vitro, tumor immunohistochemical assays, and intervention studies in vivo.
Results: LL-37 produced by myeloid cells was frequently upregulated in primary human lung cancer tissues. Moreover, its expression level correlated with poor clinical outcome. LL-37 activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling by inducing the phosphorylation of protein kinase B and subsequent phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β mediated by the toll-like receptor-4 expressed in lung tumor cells. LL-37 treatment of tumor cells also decreased the levels of Axin2. In contrast, it elevated those of an RNA-binding protein (tristetraprolin), which may be involved in the mechanism through which LL-37 induces activation of Wnt/β-catenin.
Conclusion: LL-37 may be a critical molecular link between tumor-supportive immune cells and tumors, facilitating the progression of lung cancer.
Keywords: LL-37, lung cancer, tumor microenvironment, Wnt/β-catenin
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact