13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(8):2167-2182. doi:10.7150/thno.30867 This issue Cite
Research Paper
GRP78-targeted ferritin nanocaged ultra-high dose of doxorubicin for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy
1. Key Laboratory of Protein and Peptide Pharmaceuticals, CAS-University of Tokyo Joint Laboratory of Structural Virology and Immunology, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.
2. College of Life Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.
3. Key laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research, Department of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Surgery, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, 100142, China
Abstract
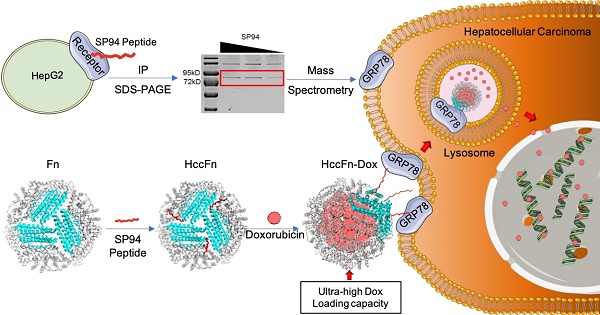
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains one of the leading causes of cancer deaths, primarily due to its high incidence of recurrence and metastasis. Considerable efforts have therefore been undertaken to develop effective therapies; however, effective anti-HCC therapies rely on identification of suitable biomarkers, few of which are currently available for drug targeting.
Methods: GRP78 was identified as the membrane receptor of HCC-targeted peptide SP94 by immunoprecipitation and mass spectrum analysis. To develop an effective anti-HCC drug nanocarrier, we first displayed GRP78-targeted peptide SP94 onto the exterior surface of Pyrococcus furiosus ferritin Fn (HccFn) by genetic engineering approach, and then loaded doxorubicin (Dox) into the cavities of HccFn via urea-based disassembly/reassembly method, thereby constructing a drug nanocarrier called HccFn-Dox.
Results: We demonstrated that HccFn nanocage encapsulated ultra-high dose of Dox (up to 400 molecules Dox/protein nanocage). In vivo animal experiments showed that Dox encapsulated in HccFn-Dox was selectively delivered into HCC tumor cells, and effectively killed subcutaneous and lung metastatic HCC tumors. In addition, HccFn-Dox significantly reduced drug exposure to healthy organs and improved the maximum tolerated dose by six-fold compared with free Dox.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our findings clearly demonstrate that GRP78 is an effective biomarker for HCC therapy, and GRP78-targeted HccFn nanocage is effective in delivering anti-HCC drug without damage to healthy tissue.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact