13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(4):1200-1214. doi:10.7150/thno.31991 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Circulating proteomic panels for diagnosis and risk stratification of acute-on-chronic liver failure in patients with viral hepatitis B
1. State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, Collaborative Innovation Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, 310003 Hangzhou, People's Republic of China
2. Department of Infectious Diseases, Zhejiang University International Hospital, 310004 Hangzhou, People's Republic of China
3. Bio-Macromolecules Analysis Laboratory of Analysis Center of Agrobiology and Environmental Sciences, Zhejiang University, 310058 Hangzhou, People's Republic of China
4. Division of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Department of Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, 310003 Hangzhou, People's Republic of China
5. Key Laboratory of Combined Multi-Organ Transplantation, Ministry of Public Health, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, 310003 Hangzhou, People's Republic of China
6. Key Laboratory of Organ Transplantation, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, 310003 Hangzhou, People's Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally: Zeyu Sun, Xiaoli Liu, Daxian Wu.
Abstract
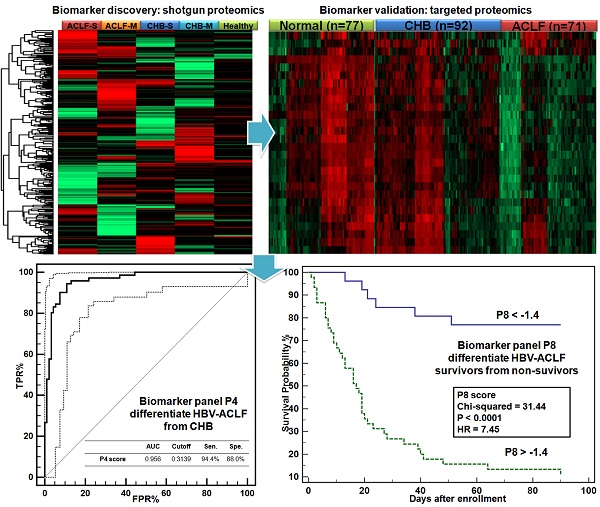
Chronic HBV infection (CHB) can lead to acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) characterized by high mortality. This study aimed to reveal ACLF-related proteomic alterations, from which protein based diagnostic and prognostic scores for HBV-ACLF were developed.
Methods: Ten healthy controls, 16 CHB, and 19 HBV-ACLF according to COSSH (Chinese group on the study of severe hepatitis B) criteria were enrolled to obtain the comprehensive proteomic portrait related to HBV-ACLF initiation and progression. Potential markers of HBV-ACLF were further selected based on organ specificity and functionality. An additional cohort included 77 healthy controls, 92 CHB and 71 HBV-ACLF was used to validate the proteomic signatures via targeted proteomic assays.
Results: Significant losses of plasma proteins related to multiple functional clusters, including fatty acid metabolism/transport, immuno-response, complement and coagulation systems, were observed in ACLF patients. In the validation study, 28 proteins were confirmed able to separate ACLF, CHB patients. A diagnostic classifier P4 (APOC3, HRG, TF, KLKB1) was built to differentiate ACLF from CHB with high accuracy (auROC = 0.956). A prognostic model P8 (GC, HRG, HPR, SERPINA6, age, NEU, INR and total protein) was built to distinguish survivors from non-survivors in 28 and 90-days follow-up (auROC = 0.882, 0.871), and to stratify ACLF patients into risk subgroups showing significant difference in 28 and 90-days mortality (HR=7.77, 7.45, both P<0.0001). In addition, P8 score correlated with ACLF grades and numbers of extra-hepatic organ failures in ACLF patients, and was able to predict ACLF-associated coagulation and brain failure within 90 days (auROC = 0.815, 0.842).
Conclusions: Proteomic signatures developed in this study reflected the deficiency of key hematological functions in HBV-ACLF patients, and show potential for HBV-ACLF diagnosis and risk prediction in complementary to current clinical based parameters.
Keywords: HBV-ACLF, biomarkers, mass spectrometry, proteomics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact