13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(21):6025-6034. doi:10.7150/thno.26607 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hypoxia-triggered single molecule probe for high-contrast NIR II/PA tumor imaging and robust photothermal therapy
1. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Nanomedicine, Shenzhen Engineering Laboratory of Nanomedicine and Nanoformulations, CAS Key Lab for Health Informatics, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen 518055, China.
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Guangdong Key Laboratory for Research and Development of Natural Drugs, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523808, China
Abstract
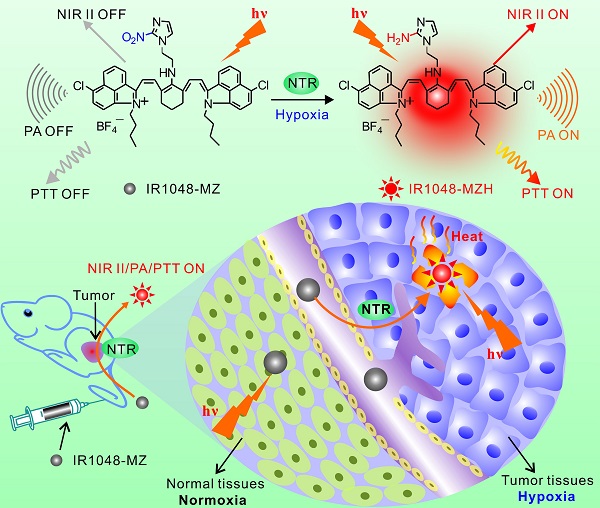
Hypoxia is a common characteristic of solid tumors. This important feature is associated with resistance to radio-chemotherapy, which results in poor prognosis and probability of tumor recurrence. Taking advantage of background-free NIR II fluorescence imaging and deeper-penetrating photoacoustic (PA) imaging, we developed a hypoxia-triggered and nitroreductase (NTR) enzyme-responsive single molecule probe for high-contrast NIR II/PA tumor imaging and hypoxia-activated photothermal therapy (PTT), which will overcome cellular resistance during hypoxia.
Methods: The single molecule probe IR1048-MZ was synthesized by conjugating a nitro imidazole group as a specific hypoxia trigger with an IR-1048 dye as a NIR II/PA signal reporter. We investigated the NIR II fluorescence, NIR absorbance and photothermal effect in different hypoxia conditions in vitro, and performed NIR II/PA tumor imaging and hypoxia-activated photothermal therapy in mice.
Results: This versatile molecular probe IR1048-MZ not only realized high-contrast tumor visualization with a clear boundary by NIR II fluorescence imaging, but also afforded deep-tissue penetration at the centimeter level by 3D PA imaging. Moreover, after being activated by NTR that is overexpressed in hypoxic tumors, the probe exhibited a significant photothermal effect for curative tumor ablation with no recurrence.
Conclusions: We have developed the first hypoxia-triggered and NTR enzyme-responsive single molecule probe for high-contrast NIR II/PA tumor imaging and hypoxia-activated photothermal therapy. By tracing the activity of NTR, IR1048-MZ may be a promising contrast agent and theranostic formulation for other hypoxia-related diseases (such as cancer, inflammation, stroke, and cardiac ischemia).
Keywords: hypoxia-triggered, single molecule probe, NIR II fluorescence imaging, PA imaging, activatable photothermal therapy.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact