13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(6):1468-1480. doi:10.7150/thno.22018 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Urinary Metabolites Associated with Blood Pressure on a Low- or High-Sodium Diet
1. Department of Nephrology, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Clinical Institute of Anhui Medical University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, P.R. China
2. The Center for Nephrology and Urology at Shenzhen University, Shenzhen University Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Guangdong, P.R. China
3. Center of Systems Molecular Medicine, Department of Physiology, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA
4. Department of Physiology and Pathophysiology, Fudan University Shanghai Medical College, Shanghai, P.R. China
5. Division of Biostatistics, Institute for Health and Society, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA
6. The Key Laboratory of Biomedical Information Engineering of Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, China
7. Division of Endocrinology, Department of Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
*equal contribution
Abstract
Dietary salt intake has significant effects on arterial blood pressure and the development of hypertension. Mechanisms underlying salt-dependent changes in blood pressure remain poorly understood, and it is difficult to assess blood pressure salt-sensitivity clinically.
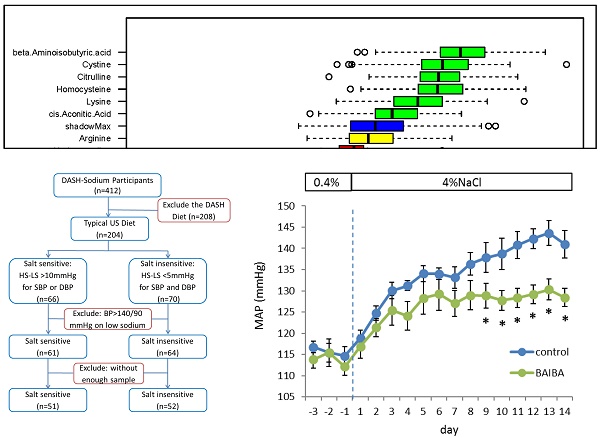
Methods: We examined urinary levels of metabolites in 103 participants of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH)-Sodium trial after nearly 30 days on a defined diet containing high sodium (targeting 150 mmol sodium intake per day) or low sodium (50 mmol per day). Targeted chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis was performed in 24 h urine samples for 47 amino metabolites and 10 metabolites related to the tricarboxylic acid cycle. The effect of an identified metabolite on blood pressure was examined in Dahl salt-sensitive rats.
Results: Urinary metabolite levels improved the prediction of classification of blood pressure salt-sensitivity based on race, age and sex. Random forest and generalized linear mixed model analyses identified significant (false discovery rate <0.05) associations of 24 h excretions of β-aminoisobutyric acid, cystine, citrulline, homocysteine and lysine with systolic blood pressure and cystine with diastolic blood pressure. The differences in homocysteine levels between low- and high-sodium intakes were significantly associated with the differences in diastolic blood pressure. These associations were significant with or without considering demographic factors. Treatment with β-aminoisobutyric acid significantly attenuated high-salt-induced hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats.
Conclusion: These findings support the presence of new mechanisms of blood pressure regulation involving metabolic intermediaries, which could be developed as markers or therapeutic targets for salt-sensitive hypertension.
Keywords: hypertension, diet, salt, metabolomics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact