13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(16):3856-3872. doi:10.7150/thno.19981 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Berunda Polypeptides: Multi-Headed Fusion Proteins Promote Subcutaneous Administration of Rapamycin to Breast Cancer In Vivo
1. Department of Pharmacology and Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Southern California, School of Pharmacy, 1985 Zonal Avenue, Los Angeles, CA 90089;
2. Department of Anatomic and Clinical Pathology, Los Angeles County & University of Southern California Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA 90033;
3. Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Southern California, School of Pharmacy, 1985 Zonal Avenue, Los Angeles, CA 90089.
Abstract
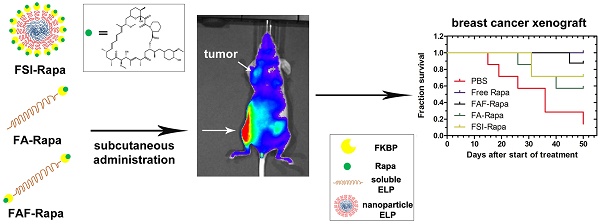
Recombinant Elastin-Like Polypeptides (ELPs) serve as attractive scaffolds for nanoformulations because they can be charge-neutral, water soluble, high molecular weight, monodisperse, biodegradable, and decorated with functional proteins. We recently reported that fusion of the FK-506 binding protein 12 (FKBP) to an ELP nanoparticle (FSI) reduces rapamycin (Rapa) toxicity and enables intravenous (IV) therapy in both a xenograft breast cancer model and a murine autoimmune disease model. Rapa has poor solubility, which leads to variable oral bioavailability or drug precipitation following parenteral administration. While IV administration is routine during chemotherapy, cytostatic molecules like Rapa would require repeat administrations in clinical settings. To optimize FKBP/Rapa for subcutaneous (SC) administration, this manuscript expands upon first-generation FSI nanoparticles (Rh ~ 25 nm) and compares them with two second-generation carriers (FA and FAF) that: i) do not self-assemble; ii) retain a hydrodynamic radius (Rh ~ 7 nm) above the renal filtration cutoff; iii) increase tumor accumulation; and iv) have either one (FA) or two (FAF) drug-binding FKBP domains per ELP protein.
Methods: The carriers were compared and evaluated for temperature-concentration phase behavior by UV-Vis spectrophotometry; equilibrium binding and thermodynamics by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry; drug retention and formulation stability by Dialysis and Dynamic Light Scattering; in vitro efficacy using a cell proliferation assay; in vivo efficacy in human MDA-MB-468 orthotopic breast cancer xenografts; downstream target inhibition using western blot; tissue histopathology; and bio-distribution via optical imaging in the orthotopic xenograft mouse model.
Results: Named after the two-headed bird in Hindu mythology, the 'Berunda polypeptide' FAF with molecular weight of 97 kDa and particle size, Rh ~ 7 nm demonstrated polypeptide conformation of a soluble hydrated coiled polymer, retained formulation stability for one month post Rapa loading, eliminated toxicity observed with free Rapa after SC administration, suppressed tumor growth, decreased phosphorylation of a downstream target, and increased tumor accumulation in orthotopic breast tumor xenografts.
Conclusion: This comprehensive manuscript demonstrates the versatility of recombinant protein-polymers to investigate drug carrier architectures. Furthermore, their facilitation of SC administration of poorly soluble drugs, like Rapa, may enable chronic self-administration in patients.
Keywords: elastin-like polypeptides, rapamycin, triple negative breast cancer, drug delivery, bio-distribution, optical imaging.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact