13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(4):855-875. doi:10.7150/thno.17558 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A Crucial Role of CXCL14 for Promoting Regulatory T Cells Activation in Stroke
1. Department of Neurosurgery, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan 40421
and Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan, Republic of China.
2. Graduate Institute of Biomedical Science, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, Republic of China.
3. Translational Medicine Research Center and Department of Neurology, China Medical University & Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan, Republic of China.
4. Department of Microbiology and Immunology, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan, Republic of China
5. Department of Biomedical Informatics, Asia University, No. 500, Lioufeng Road, Taichung, Taiwan, Republic of China.
Abstract
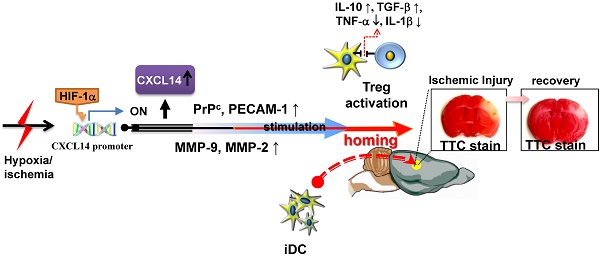
Inflammatory processes have a detrimental role in the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke. However, little is known about the endogenous anti-inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic brain. Here, we identify CXCL14 as a critical mediator of these mechanisms. CXCL14 levels were upregulated in the ischemic brains of humans and rodents. Moreover, hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) drives hypoxia- or cerebral ischemia (CI)-dependent CXCL14 expression via directly binding to the CXCL14 promoter. Depletion of CXCL14 inhibited the accumulation of immature dendritic cells (iDC) or regulatory T cells (Treg) and increased the infarct volume, whereas the supplementation of CXCL14 had the opposite effects. CXCL14 promoted the adhesion, migration, and homing of circulating CD11c+ iDC to the ischemic tissue via the upregulation of the cellular prion protein (PrPC), PECAM-1, and MMPs. The accumulation of Treg in ischemic areas of the brain was mediated through a cooperative effect of CXCL14 and iDC-secreted IL-2-induced Treg differentiation. Interestingly, CXCL14 largely promoted IL-2-induced Treg differentiation. These findings indicate that CXCL14 is a critical immunomodulator involved in the stroke-induced inflammatory reaction. Passive CXCL14 supplementation provides a tractable path for clinical translation in the improvement of stroke-induced neuroinflammation.
Keywords: CXC chemokine 14 (CXCL14), regulatory T cells (Treg), immature dendritic cells (iDC), cerebral ischemia, hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α).
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact