13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(10):1506-1513. doi:10.7150/thno.15871 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Simple, Sensitive and Accurate Multiplex Detection of Clinically Important Melanoma DNA Mutations in Circulating Tumour DNA with SERS Nanotags
1. Center for Personalized Nanomedicine. Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, Queensland, Australia
2. School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences, The University of Queensland, Queensland, Australia
3. Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute, Heidelberg, Victoria, Australia
4. Department of Surgery, University of Melbourne, Austin Health. Heidelberg, Victoria, Australia
# Authors contributed equally
Abstract
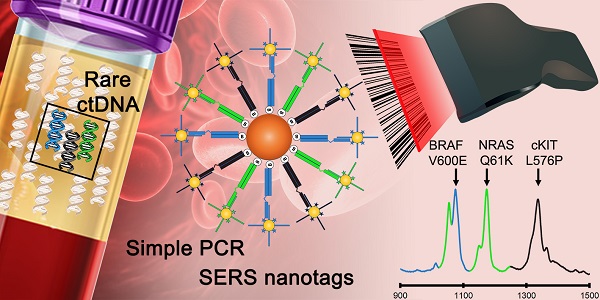
Sensitive and accurate identification of specific DNA mutations can influence clinical decisions. However accurate diagnosis from limiting samples such as circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) is challenging. Current approaches based on fluorescence such as quantitative PCR (qPCR) and more recently, droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) have limitations in multiplex detection, sensitivity and the need for expensive specialized equipment. Herein we describe an assay capitalizing on the multiplexing and sensitivity benefits of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) with the simplicity of standard PCR to address the limitations of current approaches. This proof-of-concept method could reproducibly detect as few as 0.1% (10 copies, CV < 9%) of target sequences thus demonstrating the high sensitivity of the method. The method was then applied to specifically detect three important melanoma mutations in multiplex. Finally, the PCR/SERS assay was used to genotype cell lines and ctDNA from serum samples where results subsequently validated with ddPCR. With ddPCR-like sensitivity and accuracy yet at the convenience of standard PCR, we believe this multiplex PCR/SERS method could find wide applications in both diagnostics and research.
Keywords: SERS, multiplex PCR, melanoma, BRAF, cKIT, NRAS, ctDNA
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact