13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2015; 5(12):1444-1455. doi:10.7150/thno.13398 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Noninvasive Dynamic Imaging of Tumor Early Response to Nanoparticle-mediated Photothermal Therapy
1. State Key Laboratory of Molecular Vaccinology and Molecular Diagnostics & Center for Molecular Imaging and Translational Medicine, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, 361005, China.
2. Department of Pathology, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, Xinjiang 830011, China.
3. Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Carbon-Based Functional Materials and Devices, Institute of Functional Nano and Soft Materials Laboratory (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123, China.
4. Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, Maryland 20892, United States.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
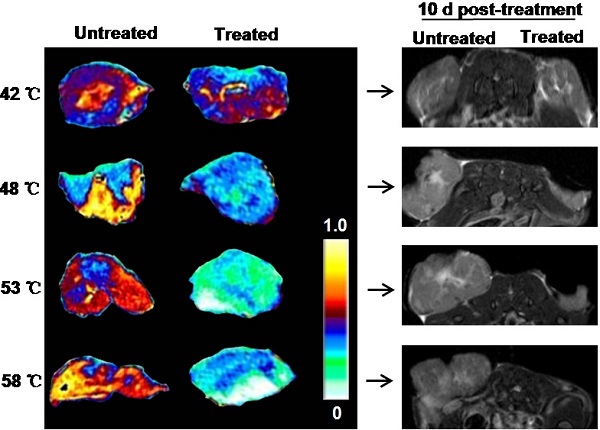
In spite of rapidly increasing interest in the use of nanoparticle-mediated photothermal therapy (PTT) for treatment of different types of tumors, very little is known on early treatment-related changes in tumor response. Using graphene oxide (GO) as a model nanoparticle (NP), in this study, we tracked the changes in tumors after GO NP-mediated PTT by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and quantitatively identified MRI multiple parameters to assess the dynamic changes of MRI signal in tumor at different heating levels and duration. We found a time- and temperature-dependent dynamic change of the MRI signal intensity in intratumor microenvironment prior to any morphological change of tumor, mainly due to quick and effective eradication of tumor blood vessels. Based on the distribution of GO particles, we also demonstrated that NP-medited PTT caused heterogeneous thermal injury of tumor. Overall, these new findings provide not only a clinical-related method for non-invasive early tracking, identifying, and monitoring treatment response of NP-mediated PTT but also show a new vision for better understanding mechanisms of NP-mediated PTT.
Keywords: Photothermal therapy, nanoparticles, magnetic resonance imaging, tumor blood vessels
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact