13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(9):2678-2693. doi:10.7150/thno.31884 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942 secretes extracellular vesicles to accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting angiogenesis
1. Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
2. Movement System Injury and Repair Research Center, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
3. Department of Sports Medicine, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
4. Hunan Key Laboratory of Organ Injury, Aging and Regenerative Medicine, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
5. Hunan Key Laboratory of Bone Joint Degeneration and Injury, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
6. National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
7. Department of Occupational and Environmental Health, Xiangya School of Public Health, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410078, China
8. Department of Dermatology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
9. Xiangya Nursing School, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410013, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
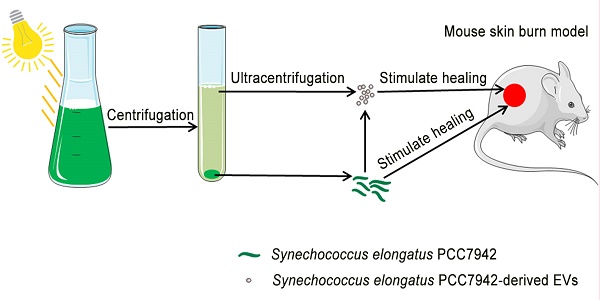
Poor wound healing affects millions of people worldwide each year and needs better therapeutic strategies. Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 is a naturally occurring photoautotrophic cyanobacterium that can be easily obtained and large-scale expanded. Here, we investigated the therapeutic efficacy of this cyanobacterium in a mouse model of acute burn injury and whether the secretion of extracellular vesicles (EVs), important mediators of cell paracrine activity, is a key mechanism of the cyanobacterium-induced regulation of wound healing.
Methods: The effects of Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 on burn wound healing in mice under light or dark conditions were evaluated by measuring wound closure rates, histological and immunofluorescence analyses. A series of assays in vivo and in vitro were conducted to assess the impact of the cyanobacterium on angiogenesis. GW4869 was used to interfere with the secretion of EVs by the cyanobacterium and the abilities of the GW4869-pretreated and untreated Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 to regulate endothelial angiogenesis were compared. The direct effects of the cyanobacterium-derived EVs (S. elongatus-EVs) on angiogenesis, wound healing and expressions of a class of pro-inflammatory factors that have regulatory roles in wound healing were also examined.
Results: Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 treatment under light and dark conditions both significantly promoted angiogenesis and burn wound repair in mice. In vitro, the cyanobacterium enhanced angiogenic activities of endothelial cells, but the effects were markedly blocked by GW4869 pretreatment. S. elongatus-EVs were capable of augmenting endothelial angiogenesis in vitro, and stimulating new blood vessel formation and burn wound healing in mice. The expression of interleukin 6 (IL-6), which has an essential role in angiogenesis during skin wound repair, was induced in wound tissues and wound healing-related cells by S. elongatus-EVs and Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942.
Conclusion: Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 has the potential as a promising strategy for therapeutic angiogenesis and wound healing primarily by the delivery of functional EVs, not by its photosynthetic activity. The promotion of IL-6 expression may be a mechanism of the cyanobacterium and its EVs-induced pro-angiogenic and -wound healing effects.
Keywords: Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942, extracellular vesicles, wound healing, angiogenesis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact