13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(3):633-645. doi:10.7150/thno.31485 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A Synthetic Receptor as a Specific Antidote for Paraquat Poisoning
1. State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, and Institute of Chinese Medical Sciences, University of Macau, Taipa, Macau, China.
2. Department of Pharmaceutics, College of Pharmacy, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing 400038, China.
Abstract
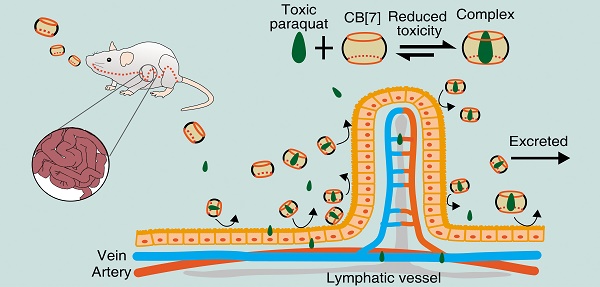
Accidental or suicidal ingestion of the world's most widely used herbicide, paraquat (PQ), may result in rapid multi-organ failure with a 60% fatality rate due to the absence of an effective detoxification solution. Effective, specific antidotes to PQ poisoning have been highly desired.
Methods: The binding constant of PQ and a synthetic receptor, cucurbit[7]uril (CB[7]), was first determined in various pH environments. The antidotal effects of CB[7] on PQ toxicity were firstly evaluated with in-vitro cell lines. With in-vivo mice models, the pharmacokinetics and the biodistribution of PQ in major organs were determined to evaluate the influence of CB[7] on the oral bioavailability of PQ. Major organs' injuries and overall survival rates of the mice were systemically examined to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of CB[7] on PQ poisoning.
Results: We demonstrate that CB[7] may complex PQ strongly under various conditions and significantly reduce its toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Oral administration of PQ in the presence of CB[7] in a mouse model significantly decreased PQ levels in the plasma and major organs and alleviated major organs' injuries, when compared to those of mice administered with PQ alone. Further studies indicated that oral administration of CB[7] within 2 h post PQ ingestion significantly increased the survival rates and extended the survival time of the mice, in contrast to the ineffective treatment by activated charcoal, which is commonly recommended for PQ decontamination.
Conclusion: CB[7] may be used as a specific oral antidote for PQ poisoning by strongly binding with PQ and inhibiting its absorption in the gastrointestinal tracts.
Keywords: paraquat toxicity, cucurbit[7]uril, antidote, detoxification
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact