13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(19):5307-5319. doi:10.7150/thno.26823 This issue Cite
Review
EBNA1-targeted inhibitors: Novel approaches for the treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-associated cancers
1. Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR, China.
2. Department of Biology, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR, China.
3. Department of Applied Biological and Chemical Technology, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Hong Kong SAR, China.
4. Department of Anatomical and Cellular Pathology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China.
Abstract
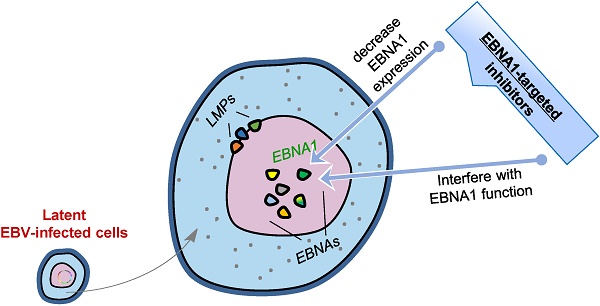
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects more than 90% of humans worldwide and establishes lifelong latent infection in the hosts. It is closely associated with endemic forms of a wide range of human cancers and directly contributes to the formation of some. Despite its critical role in cancer development, no EBV- or EBV latent protein-targeted therapy is available. The EBV-encoded latent protein, Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1), is expressed in all EBV-associated tumors and acts as the only latent protein in some of these tumors. This versatile protein functions in the maintenance, replication, and segregation of the EBV genome and can therefore serve as an attractive therapeutic target to treat EBV-associated cancers. In the last decades, efforts have been made for designing specific EBNA1 inhibitors to decrease EBNA1 expression or interfere with EBNA1-dependent functions. In this review, we will briefly introduce the salient features of EBNA1, summarize its functional domains, and focus on the recent developments in the identification and design of EBNA1 inhibitors related to various EBNA1 domains as well as discuss their comparative merits.
Keywords: EBNA1-targeted inhibitor, fluorescent probe, EBV-associated cancers, EBV, EBNA1
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact