13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(18):5025-5038. doi:10.7150/thno.26837 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Novel skin patch combining human fibroblast-derived matrix and ciprofloxacin for infected wound healing
1. Center for Biomaterials, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul 02792, Republic of Korea
2. Unit of Education, Research, and Training, Universitas Indonesia Hospital, Universitas Indonesia, Depok 16424, Indonesia
3. Medical Technology Research Cluster, Indonesia Medical Education and Research Institute, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta Pusat 10430, Indonesia
4. Department of Biomedical Science, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02447, Republic of Korea
5. Department of Maxillofacial Biomedical Engineering, School of Dentistry/Department of Life and Nanopharmaceutical Sciences, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02447, Republic of Korea
6. Division of Bio-Medical Science and Technology, KIST School, Korea University of Science and Technology (UST), Seoul 02792, Republic of Korea
†These authors contributed equally
Abstract
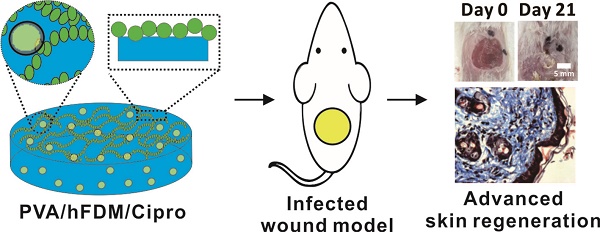
Skin injuries are frequently encountered in daily life, but deep wounds often poorly self-heal and do not recover completely. In this study, we propose a novel skin patch that combines antibiotic, cell-derived extracellular matrix (ECM) and biocompatible polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel.
Methods: Decellularized human lung fibroblast-derived matrix (hFDM) was prepared on tissue culture plate (TCP) and PVA solution was then poured onto it. After a freeze-thaw process, PVA was peeled off from TCP along with hFDM tightly anchored to PVA. Subsequently, ciprofloxacin (Cipro)-incorporated PVA/hFDM (PVA/Cipro/hFDM) was fabricated via diffusion-based drug loading.
Results: In vitro analyses of PVA/Cipro/hFDM show little cytotoxicity of ciprofloxacin, stability of hFDM, rich fibronectin in hFDM, and good cell attachment, respectively. In addition, hFDM proved to be beneficial in promoting cell migration of dermal fibroblasts and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) using transwell inserts. The antibacterial drug Cipro was very effective in suppressing colony growth of gram-negative and -positive bacteria as identified via an inhibition zone assay. For animal study, infected wound models in BALB/c mice were prepared and four test groups (control, PVA, PVA/Cipro, PVA/Cipro/hFDM) were administered separately and their effect on wound healing was examined for up to 21 days. The results support that Cipro successfully reduced bacterial infection and thus encouraged faster wound closure. Further analysis using histology and immunofluorescence revealed that the most advanced skin regeneration was achieved with PVA/Cipro/hFDM, as assessed via re-epithelialization, collagen texture and distribution in the epidermis, and skin adnexa (i.e., glands and hair follicles) regeneration in the dermis.
Conclusion: This work demonstrates that our skin patch successfully consolidates the regenerative potential of ECM and the antibacterial activity of Cipro for advanced wound healing.
Keywords: wound healing, skin patch, human fibroblast-derived matrix, ciprofloxacin, polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact