13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(18):4884-4897. doi:10.7150/thno.27581 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Enhanced bioreduction-responsive diselenide-based dimeric prodrug nanoparticles for triple negative breast cancer therapy
1. Key Laboratory of Smart Drug Delivery, Ministry of Education, State Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology, School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
2. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1304 W. Green Street, Urbana, Illinois 61801, United States
3. School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, China
Abstract
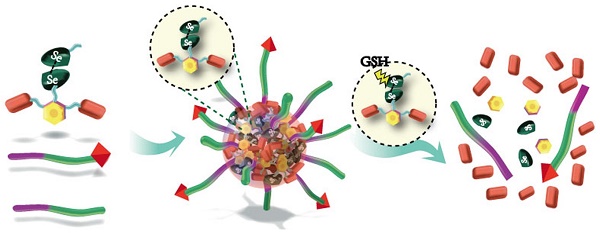
Efficient drug accumulation in tumor is essential for chemotherapy. We developed redox-responsive diselenide-based high-loading prodrug nanoparticles (NPs) for targeted triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) treatment.
Method: Redox-responsive diselenide bond (Se-Se) containing dimeric prodrug (PTXD-Se) was synthesized and co-precipitated with TNBC-targeting amphiphilic copolymers to form ultra-stable NPs (uPA-PTXD NPs). The drug loading capacity and redox-responsive drug release behavior were studied. TNBC targeting effect and anti-tumor effect were also evaluated in vitro and in vivo.
Results: On-demand designed paclitaxel dimeric prodrug could co-precipitate with amphiphilic copolymers to form ultra-stable uPA-PTXD NPs with high drug loading capacity. Diselenide bond (Se-Se) in uPA-PTXD NPs could be selectively cleaved by abnormally high reduced potential in tumor microenvironment, releasing prototype drug, thus contributing to improved anti-cancer efficacy. Endowed with TNBC-targeting ligand uPA peptide, uPA-PTXD NPs exhibited reduced systemic toxicity and enhanced drug accumulation in TNBC lesions, thus showed significant anti-tumor efficacy both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: The comprehensive advantage of high drug loading, redox-controlled drug release and targeted tumor accumulation suggests uPA-PTXD NPs as a highly promising strategy for effective TNBC treatment.
Keywords: diselenide bond, nanoparticles, prodrugs, redox responsive, triple negative breast cancer
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact