13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(2):486-504. doi:10.7150/thno.22059 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MiR-31-5p-ACOX1 Axis Enhances Tumorigenic Fitness in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Via the Promigratory Prostaglandin E2
1. Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Guishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan, ROC
2. Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Guishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan, ROC
3. Molecular Medicine Research Center, Chang Gung University, Guishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan, ROC
4. Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery, Linkou Medical Center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan, ROC
5. Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, Chi-Mei Medical Center, Liouying, Tainan, Taiwan, ROC
6. School of Dentistry, National Yang Ming University, Beitou, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC
7. Liver Research Center, Linkou Medical Center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan, ROC
8. ACT Genomics, Co., Ltd., Neihu, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC
9. Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Guishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan, ROC
10. Department of Neurosurgery, Linkou Medical Center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan, ROC
Abstract
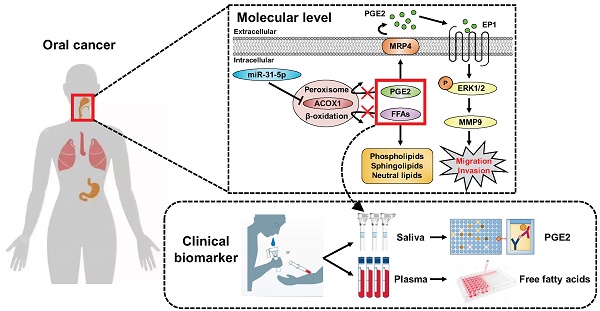
During neoplastic development, a multitude of changes in genome-encoded information are progressively selected to confer growth and survival advantages to tumor cells. microRNAs-mRNAs regulatory networks, given their role as a critical layer of robust gene expression control, are frequently altered in neoplasm. However, whether and how these gene perturbations impact metabolic homeostasis remains largely unresolved.
Methods: Through targeted miRNA expression screening, we uncovered an oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)-associated miRNAome, among which miR-31-5p was identified based on extent of up-regulation, functional impact on OSCC cell migration and invasion, and direct regulation of the rate-limiting enzyme in peroxisomal β-oxidation, ACOX1.
Results: We further found that both miR-31-5p and ACOX1 underpin, in an antagonistic manner, the overall cellular lipidome profiles as well as the migratory and invasive abilities of OSCC cells. Interestingly, the extracellular levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), a key substrate of ACOX1, were controlled by the miR-31-5p-ACOX1 axis, and were shown to positively influence the extent of cell motility in correlation with metastatic status. The promigratory effect of this metabolite was mediated by an elevation in EP1-ERK-MMP9 signaling. Of note, functional significance of this regulatory pathway was further corroborated by its clinicopathologically-correlated expression in OSCC patient specimens.
Conclusions: Collectively, our findings outlined a model whereby misregulated miR-31-5p-ACOX1 axis in tumor alters lipid metabolomes, consequently eliciting an intracellular signaling change to enhance cell motility. Our clinical analysis also unveiled PGE2 as a viable salivary biomarker for prognosticating oral cancer progression, further underscoring the importance of lipid metabolism in tumorigenesis.
Keywords: miRNA-mRNA network, ACOX1, lipid metabolism, oral squamous cell carcinoma, prostaglandins
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact