13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(2):384-398. doi:10.7150/thno.22222 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Desacetylvinblastine Monohydrazide Disrupts Tumor Vessels by Promoting VE-cadherin Internalization
1. College of Pharmacy, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China;
2. Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Pharmacodynamic Constituents of Traditional Chinese Medicine and New Drugs Research, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China;
3. The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China;
4. Department of Pharmacology, Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, School of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio 44106, USA.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
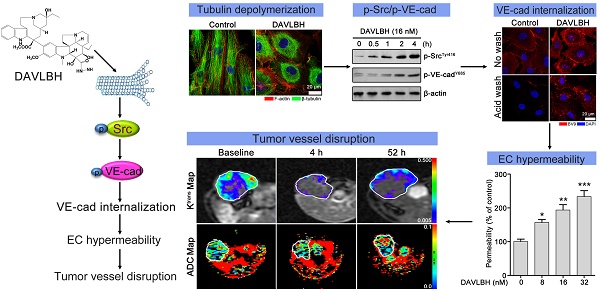
Vinca alkaloids, the well-known tubulin-binding agents, are widely used for the clinical treatment of malignant tumors. However, little attention has been paid to their vascular disrupting effects, and the underlying mechanisms remain largely unknown. This study aims to investigate the vascular disrupting effect and the underlying mechanisms of vinca alkaloids.
Methods: The capillary disruption assay and aortic ring assay were performed to evaluate the in vitro vascular disrupting effect of desacetylvinblastine monohydrazide (DAVLBH), a derivate of vinblastine, and the in vivo vascular disrupting effect was assessed on HepG2 xenograft model using magnetic resonance imaging, hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry. Tubulin polymerization, endothelial cell monolayer permeability, western blotting and immunofluorescence assays were performed to explore the underlying mechanisms of DAVLBH-mediated tumor vascular disruption.
Results: DAVLBH has potent vascular disrupting activity both in vitro and in vivo. DAVLBH disrupts tumor vessels in a different manner than classical tubulin-targeting VDAs; it inhibits microtubule polymerization, promotes the internalization of vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin) and inhibits the recycling of internalized VE-cadherin to the cell membrane, thus increasing endothelial cell permeability and ultimately resulting in vascular disruption. DAVLBH-mediated promotion of VE-cadherin internalization and inhibition of internalized VE-cadherin recycling back to the cell membrane are partly dependent on inhibition of microtubule polymerization, and Src activation is involved in DAVLBH-induced VE-cadherin internalization.
Conclusions: This study sheds light on the tumor vascular disrupting effect and underlying mechanisms of vinca alkaloids and provides new insight into the molecular mechanism of tubulin-targeting VDAs.
Keywords: Vascular disrupting agents, vinca alkaloids, desacetylvinblastine monohydrazide, tubulin polymerization, VE-cadherin internalization.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact