13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(15):3768-3780. doi:10.7150/thno.20796 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Bidirectional Regulation between MYL5 and HIF-1α Promotes Cervical Carcinoma Metastasis
1. Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou 510060, China;
2. The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University Guangzhou 510080, People's Republic of China;
3. The Second Affiliated Hospital, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330000, P. R. China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
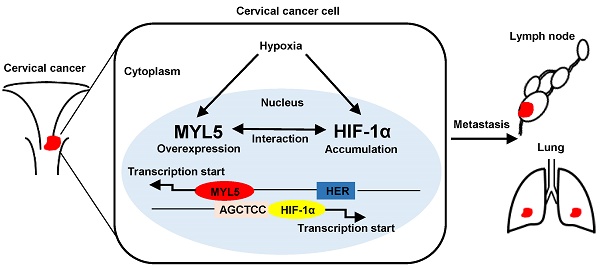
Myosin light chains (MLC) serve important regulatory functions in a wide range of cellular and physiological processes. Recent research found that MLC are also chromatin-associated nuclear proteins which regulate gene transcription. In this study, the MLC member myosin regulatory light chain 5 (MYL5) expression was upregulated in late stage cervical cancer patients, positively correlated with pelvic lymph node metastasis, and identified as a poor survival indicator. MYL5 overexpression promoted metastasis in cervical cancer in vitro and in vivo models, whereas MYL5 silencing had the converse effect. We demonstrated a bidirectional regulation between MYL5 and hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). HIF-1α activates MYL5 via binding to the hypoxia response element (HRE) in the promoter of MYL5, and MYL5 could sustain HIF-1α expression by tethering to recognition sequence AGCTCC in the HIF-1α promoter region. Clinical data confirmed a positive correlation between MYL5 and HIF-1α. In summary, our data show that MYL5 may act as a prognosis predictive factor in cervical carcinoma, and strategies that inhibit the interaction of MYL5 and HIF-1α may benefit the cervical carcinoma patients with metastasis.
Keywords: MYL5, cervical cancer, oxygen regulation.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact