13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(12):3118-3137. doi:10.7150/thno.19396 This issue Cite
Review
3D Cell Printed Tissue Analogues: A New Platform for Theranostics
1. Division of Integrative Biosciences and Biotechnology, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang, Gyeongbuk 790-781, Republic of Korea;
2. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang, Gyeongbuk 790-781, Republic of Korea.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
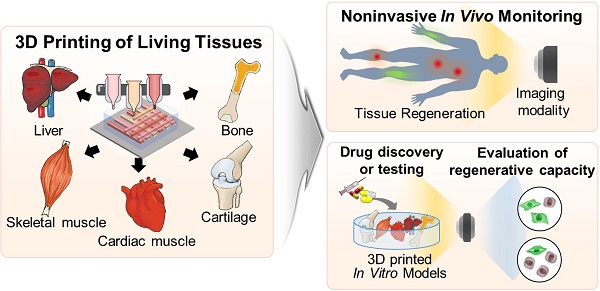
Stem cell theranostics has received much attention for noninvasively monitoring and tracing transplanted therapeutic stem cells through imaging agents and imaging modalities. Despite the excellent regenerative capability of stem cells, their efficacy has been limited due to low cellular retention, low survival rate, and low engraftment after implantation. Three-dimensional (3D) cell printing provides stem cells with the similar architecture and microenvironment of the native tissue and facilitates the generation of a 3D tissue-like construct that exhibits remarkable regenerative capacity and functionality as well as enhanced cell viability. Thus, 3D cell printing can overcome the current concerns of stem cell therapy by delivering the 3D construct to the damaged site. Despite the advantages of 3D cell printing, the in vivo and in vitro tracking and monitoring of the performance of 3D cell printed tissue in a noninvasive and real-time manner have not been thoroughly studied. In this review, we explore the recent progress in 3D cell technology and its applications. Finally, we investigate their potential limitations and suggest future perspectives on 3D cell printing and stem cell theranostics.
Keywords: Three-dimensional (3D) cell printing, stem cell theranostics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact