13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(5):1114-1132. doi:10.7150/thno.18175 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The YAP1/SIX2 axis is required for DDX3-mediated tumor aggressiveness and cetuximab resistance in KRAS-wild-type colorectal cancer
1. Graduate Institute of Cancer Biology and Drug Discovery, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
2. Department of Public Health, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
3. Department of Surgery, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
Abstract
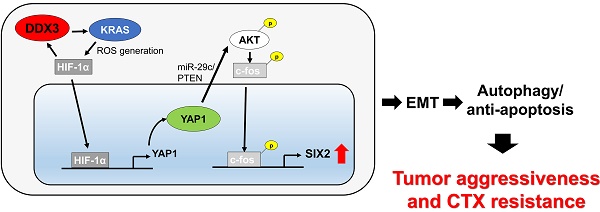
The mechanism underlying tumor aggressiveness and cetuximab (CTX) resistance in KRAS-wild-type (KRAS -WT) colorectal cancer remains obscure. We here provide evidence that DDX3 promoted soft agar growth and invasiveness of KRAS-WT cells, as already confirmed in KRAS-mutated cells. Mechanistically, increased KRAS expression induced ROS production, which elevated HIF-1α and YAP1 expression. Increased HIF-1α persistently promoted DDX3 expression via a KRAS/ROS/HIF-1α feedback loop. DDX3-mediated aggressiveness and CTX resistance were regulated by the YAP1/SIX2 axis in KRAS-WT cells and further confirmed in animal models. Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analysis indicated that DDX3, KRAS, and YAP1 expression had prognostic value for OS and RFS in KRAS-WT and KRAS-mutated tumors, but SIX2 and YAP1/SIX2 were prognostic value only in KRAS-WT patients. The observation from patients seemed to support the mechanistic action of cell and animal models. We therefore suggest that combining YAP1 inhibitors with CTX may therefore suppress DDX3-mediated tumor aggressiveness and enhance CTX sensitivity in KRAS-WT colorectal cancer.
Keywords: DDX3, YAP1, SIX2, KRAS, and colorectal cancer.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact