13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(7):1053-1064. doi:10.7150/thno.14843 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ATP-Responsive and Near-Infrared-Emissive Nanocarriers for Anticancer Drug Delivery and Real-Time Imaging
1. Department of Polymer Science & Engineering and Key Laboratory of High Performance Polymer Materials & Technology of MOE, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Life Sciences, School of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China;
2. Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC 27695, USA;
3. Division of Molecular Pharmaceutics and Center for Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery, Eshelman School of Pharmacy, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC 27599, USA;
4. Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC 27599, USA.
*These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
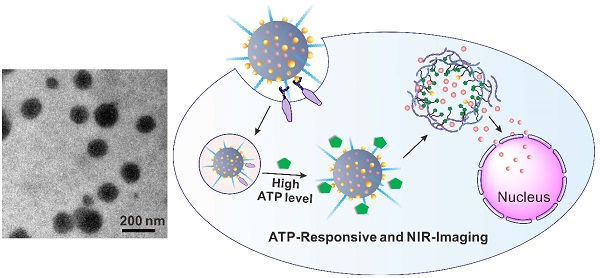
Stimuli-responsive and imaging-guided drug delivery systems hold vast promise for enhancement of therapeutic efficacy. Here we report an adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP)-responsive and near-infrared (NIR)-emissive conjugated polymer-based nanocarrier for the controlled release of anticancer drugs and real-time imaging. We demonstrate that the conjugated polymeric nanocarriers functionalized with phenylboronic acid tags on surface as binding sites for ATP could be converted to the water-soluble conjugated polyelectrolytes in an ATP-rich environment, which promotes the disassembly of the drug carrier and subsequent release of the cargo. In vivo studies validate that this formulation exhibits promising capability for inhibition of tumor growth. We also evaluate the metabolism process by monitoring the fluorescence signal of the conjugated polymer through the in vivo NIR imaging.
Keywords: drug delivery, nanomedicine, stimuli-responsive, ATP-responsive, theranostics, conjugated polymers.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact